In business today, it is a requirement to demonstrate continuous improvement in environmentally sustainable practices and meet legislation demands. For this to occur, a business needs to first look at the systems they have in place for sustainability and design a plan to improve on areas of work practice. This needs to be monitored and reviewed to ensure progress is being made. For this to occur, documentation and recording of improvement is necessary to demonstrate and observe progress.
Watch
Watch this video from Apple CEO Steve Jobs explaining the concept of Continuous Improvement.
Next, look at this animation explaining the process of CI- Continuous Improvement and ways to create the culture.

Implementation is a large-scale system; it needs to be a concept of all in order to reach and achieve the goals. Goals are supported by the collaboration of ideas, opinions and the voices of the stakeholders, especially those that will be implementing the strategies. These stakeholders could include external or internal bodies, individuals, and governing bodies.
Involving team members with the work practice by supporting them to identify areas for improved resource efficiency will provide a wider range of ideas and encourage ownership.
Team members can support the process by:
- Assisting to measure current resource usage
- Suggesting alternative ideas and solutions to issues
- Implementing other strategies to improve resource usage
- Collaborating in the development of the Action Plan.
Communicating and collaborating with stakeholders is key to successful sustainable goal planning and achievement. Therefore, workplaces should:
- Book regular meetings to discuss areas for improvement and the overall implementation plan
- Seek feedback throughout the cycle (the development and audit, after implementation and review)
- Decide on the actions they will take together with stakeholders.
You can seek further feedback from stakeholders by utilising:
- Surveys
- Questionnaires
- Focus Groups
- Community Forums
How to Monitor Efficiency Targets?
Monitoring efficiency targets involves several steps to ensure that goals are being met and that corrective action can be taken if necessary.
Here's are some examples of how you can approach this:
Define Clear and Measurable Targets
- Ensure that efficiency targets are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Clearly define what you want to achieve and how you will measure success.
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Identify key metrics that will be used to track progress toward efficiency targets. These could include indicators such as energy consumption, resource utilization, waste generation, productivity levels, or cost savings.
Watch
Watch this quick video to give an overview of Smart Goals.
Next watch this video providing some real life examples on SMART goals and how to achieve them.
Implement Monitoring Systems
- Put in place systems and processes to collect relevant data on KPIs. This might involve using software systems, sensors, meters, or manual data collection methods, depending on the nature of the targets.
Regular Data Collection and Analysis: Collect data on KPIs regularly, whether it's daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on the time frame of your targets. Analyze the data to track trends, identify patterns, and assess performance against targets.
Watch
Watch this next video to give you a quick overview/refresh on the concept of KPI.
Compare Actual Performance with Targets
- Compare actual performance data with the targets set. Calculate variances and assess whether performance is meeting, exceeding, or falling short of expectations.
- Identify Root Causes of Variances: Investigate the underlying reasons for any discrepancies between actual performance and targets. Determine whether variances are due to internal factors (e.g., operational issues, process inefficiencies) or external factors (e.g., market conditions, regulatory changes).
Take Corrective Action
- If performance is not meeting targets, take corrective action to address identified issues and improve performance. This might involve implementing process improvements, adjusting resource allocation, investing in new technologies, or revising targets if necessary.
Communicate Results and Progress
- Communicate performance results and progress toward efficiency targets to relevant organisational stakeholders. This fosters transparency, accountability, and awareness of performance trends.
Watch
Watch this small video explaining how to speak with stakeholders, when communicating projects and results.
Continuous Improvement
- Continuously review and refine monitoring systems, KPIs, and targets based on feedback and lessons learned. Regularly reassess goals and adjust them as needed to reflect changing circumstances, emerging opportunities, or evolving priorities.
Celebrate Successes and Learn from Failures
- Celebrate achievements when efficiency targets are met or exceeded. Likewise, use any failures or setbacks as learning opportunities to identify areas for improvement and refine strategies for future success.
Watch
Watch the next couple of videos highlighting the importance of celebrating the wins!
Organisations can effectively monitor efficiency targets, track progress, and take proactive measures to optimize performance and achieve desired outcomes.

There are many advantages to making sure that your team members have the support they need. Clearly, it makes work easier, safer, and more enjoyable; and it helps your people to be much more effective. After all, we all want to do our jobs well, and we want to make a difference in the world.
Team members can support the business and processes by:
- Assisting in measuring current resource usage
- Suggesting alternative ideas and solutions to issues
- Implementing other strategies to improve resource usage
- Collaborating in the development of the Action Plan.
How to support your team?
- Encourage collaboration
- Communicate often
- Provide learning opportunities
- Recognise achievements
- Celebrate their success
- Offer help
- Prioritise tasks
- Trust your team
- Be open to change
Watch
The next video gives some tips on strategies to assist with effective teamwork.
Supporting team members to identify possible areas for improved resource efficiency in work areas involves fostering a culture of collaboration, innovation, and continuous improvement.
Here are some strategies to achieve this:
Training and Awareness
- Training and awareness is a support process that ensures staff members have the knowledge and skills to perform their work, including work in other processes such as incident management, controls management, and risk management. Training and awareness typically takes place at various levels of an organisation.
- Provide training and raise awareness among team members about the importance of resource efficiency and sustainability. Educate them about the potential environmental, economic, and social benefits of reducing resource consumption and waste.
Watch
Next, watch this small Ted Talk about how to train employees effectively.
Watch this video talks about how to train staff effectively.
Encourage Participation
- Encourage team members to actively participate in identifying opportunities for improved resource efficiency. Create a supportive environment where everyone feels empowered to contribute ideas and suggestions.
How to encourage participation from your team?
- Encourage participation and create a space where staff can feel comfortable providing feedback.
- Help your team feel good about their contributions.
- Employee involvement strengthens the connection with the business.
- Reward creativity. Let your support staff know it’s safe and, in fact, encouraged to come up with the new ideas and put them into action.
- To create a supportive environment, you need to involve your employees in the design and delivery of training and development program.
Watch
Watch this small clip about engaging team members and making the environment inclusive.
Regular Brainstorming Sessions
- Brainstorming is a large- or small-group discussion that encourages students to generate a wide range of perspectives or potential next steps or solutions regarding a specific topic. The teacher may begin a brainstorming session by posing a question or a problem, or by introducing a topic.
- Hold regular brainstorming sessions or meetings dedicated to discussing resource efficiency opportunities. Encourage team members to share their insights, observations, and innovative ideas for reducing waste, optimizing energy usage, or improving processes.
Watch
Watch the below video about Brainstorming- techniques and rules.
Conduct Waste Audits
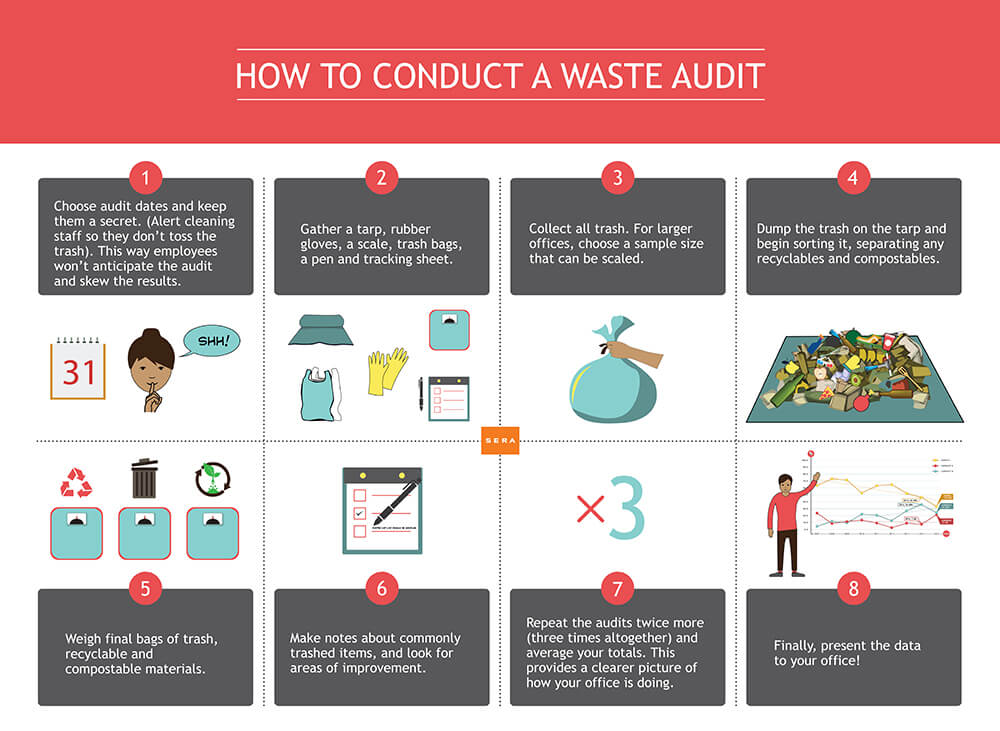
- A waste audit is a formal, structured process used to quantify the amount and types of waste an organisation generates. Audit information will help identify current waste practices and how they can be improved. Being waste-wise can mean more efficient and effective organisation.
- Conduct waste audits to assess current resource usage and identify areas where waste can be reduced or eliminated. Analyze waste streams, energy consumption, water usage, and material flows to pinpoint opportunities for improvement.
Utilize Employee Suggestions Programs
- An employee suggestion program is any system or process encouraging employees to submit helpful ideas for new products, identify potential improvements to the workplace, or call attention to any problems or difficulties they may be experiencing.
- Implement employee suggestion programs or suggestion boxes where team members can submit ideas for improving resource efficiency anonymously. Recognize and reward employees for their contributions and successful suggestions.
- Examples of possible systems include the familiar suggestion box with written forms; the old-fashioned bulletin board for posting ideas and results; a special toll-free telephone line to allow employees to phone in suggestions; or more sophisticated systems based on e-mail or postings to a dedicated Web site.
Gemba Walks
- A Gemba Walk is a workplace walkthrough that aims to observe employees, ask about their tasks, and identify productivity gains. Gemba Walk is derived from the Japanese word “Gemba” or “Gembutsu” which means “the real place”, so it is often literally defined as the act of seeing where the actual work happens.
- Conduct Gemba walks, where managers and team members observe work areas firsthand to identify inefficiencies and waste. Encourage open communication and dialogue during these walks to discuss potential improvements collaboratively.
Watch
The next video is a small explanation of what is a Gemba Walk and what it means.
Provide Resources and Support
- Provide team members with the necessary resources, tools, and support to implement their ideas for improving resource efficiency. This might include access to training, funding for pilot projects, or assistance from cross-functional teams.
Watch
The next video is a talk from Dr Athina Kanioura from Pepsi explaining how to motivate employees.
Set Clear Goals and Targets
Importance of Goal Setting in an Organization
- Provides direction
- Increases motivation
- Measures progress
- Enhances decision-making
- Creates coordination and synergy
- Prioritize work
- Better time management
Set clear goals and targets for improving resource efficiency within work areas. Establish measurable objectives, such as reducing energy consumption by a certain percentage or decreasing waste generation, to guide efforts and track progress.
Watch
Watch this video from Gro Up Leadership explaining how to set up goals for Employees.
Promote Knowledge Sharing
-
Types of Knowledge Sharing: This can be done through communication, education, or training. For example, a company may have explicit knowledge and share best practices with other companies in its industry. Another example of explicit knowledge sharing is when an individual writes a how-to guide and shares it online.
- Encourage knowledge sharing and best practice sharing among team members. Facilitate opportunities for teams to learn from each other's successes and challenges, whether through regular meetings, internal newsletters, or online collaboration platforms.
Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
- Continuous monitoring provides the necessary data and insights that fuel feedback loops, enabling teams to make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and measure the impact of their changes.
- Implement systems for continuous monitoring of resource usage and performance indicators. Provide regular feedback to team members on their progress toward improving resource efficiency and celebrate achievements along the way.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can empower their team members to proactively identify and address areas for improved resource efficiency in their work areas, leading to cost savings, environmental benefits, and enhanced operational sustainability.

Communicating and collaborating with stakeholders is key to successful sustainable goal planning and achievement. Therefore, workplaces should:
- Book regular meetings to discuss areas for improvement and the overall implementation plan
- Seek feedback throughout the cycle (the development and audit, after implementation and review)
- Decide on the actions they will take together with stakeholders.
You can seek further feedback from stakeholders by utilising:
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Focus groups
- Community forums
Seeking and acting on feedback from stakeholders on the implementation of resource efficiency initiatives is crucial for ensuring their success and sustainability. Here's how you can effectively gather and act on feedback:
Identify Key Stakeholders
- Identify all relevant stakeholders who are impacted by or have an interest in the resource efficiency initiatives. This may include employees, managers, customers, suppliers, regulators, community members, and other relevant parties.
Watch
Watch this small video explaining the concept of a Stakeholder and the difference between a Share Holder and Stakeholder
Establish Communication Channels
What are “communication channels”? In a nutshell, communication channels are mediums through which you can convey a message to its intended audience. For example, phone calls, text messages, emails, video, radio, and social media are all types of communication channels.
Establish clear and accessible communication channels for stakeholders to provide feedback. This could include suggestion boxes, online surveys, feedback forms, email addresses, dedicated meetings, or even social media platforms, depending on the preferences of your stakeholders.
A communication channel is the medium through which you send a message to another person. There are written, verbal, and nonverbal channels of communication. An electronic channel is another means to communicate verbally, nonverbally, or in writing. You can use multiple channels of communication at the same time.
Communication Channel
Communication channels are used for various purposes. These include:
- Receive and send important messages
- Answer your team's questions in real-time
- Prompt discussions that encourage teammates to communicate with each other
- Share materials like presentation files and important documents
Examples of Communication Channels
- Video Conferencing
- Phone Calls
- Instant Messaging
- SMS Texting
Regularly Seek Feedback
One of the best ways to encourage your team to share feedback with you is to nurture open communication. You can do this by asking the team members direct questions that show you're genuinely interested to know how they feel about their work environment and you being their leader.
Actively solicit feedback from stakeholders at various stages of the implementation process. This could include seeking input during the planning phase, after the initial rollout, and periodically thereafter to assess ongoing progress and make adjustments as needed.
Listen Actively and Respectfully
Active listening requires you to listen attentively to a speaker, understand what they're saying, respond and reflect on what's being said, and retain the information for later. This keeps both the listener and speaker actively engaged in the conversation, and it's an essential building block of compassionate leadership.
When gathering feedback, listen actively and attentively to what stakeholders have to say. Respect their perspectives, experiences, and suggestions, even if they differ from your own. Avoid being defensive and demonstrate a willingness to consider and act on feedback.
Watch
The next video explains Active Listening and the concept of it.
Listening is a sign of respect. It shows that you value what the speaker has to say. If you take the time to listen to someone, take the time to listen properly. Set aside what you are doing so you can focus on the speaker, showing them that they are important to you.
Respectful listening looks like
- Nod Occasionally
- Smile
- Using Facial Expressions
- Posture is open and engaged
- Using small verbal cues like yes, uh huh
When we listen, we hear someone into existence.Laurie Buchanan, PHD
Watch
Next watch this TedTalk explaining 4 great things all great listeners need to know.
Analyse Feedback
Feedback analysis involves identifying the needs and frustrations of customers, so that businesses can improve customer satisfaction and reduce churn. It's often done automatically, enabling companies to sort huge amounts of data from various channels in a timely and accurate way.
Analyze the feedback received from stakeholders to identify common themes, patterns, and areas for improvement. Look for insights and trends that can inform decision-making and help prioritize actions to address key concerns or opportunities.
Naturally, the comments you receive will be both positive and negative. The first step to analyzing your employee feedback is to organize the comments based on sentiment. This helps you identify two things -- what actions you should continue doing and what needs to be addressed as soon as possible.
Watch
Watch the next video, a Ted Talk explaining the secret to giving great feedback.
Take Prompt Action
Take prompt and appropriate action based on the feedback received. This might involve making adjustments to the implementation plan, revising policies or procedures, providing additional resources or support, or addressing specific issues or concerns raised by stakeholders.
Tips to help take action on feedback
- Make a firm commitment to take thoughtful and disciplined action on the results of any feedback you receive before you ask for the feedback
- Make your commitment public
- Become better at listening by talking less…the less you talk, the more you learn
- Seek to understand your personality and its associated natural behaviours…while you can’t change your personality, you can change your behaviours
- Target one and only one behavior to change or improve at a time
- Give yourself 30 days of daily practice to master a new behaviour or improve upon an existing one
- Have someone in your corner to encourage you and hold you accountable
If you don’t do anything, you stay in the state you are in.Newton’s first law
Watch
Watch this Ted Talking, which explains the concept of talking action.
Communicate Changes and Progress
Communicate any changes or improvements made in response to stakeholder feedback. Keep stakeholders informed about the actions taken, the reasons behind them, and the expected outcomes. Transparency and open communication build trust and demonstrate a commitment to addressing stakeholders' needs and priorities.
Critical steps in explaining change
- Explain why: Ensure that you're able to clearly explain the change and why it's important.
- Make Space: People need to let go of old, familiar ways before they can adopt new ones. Be crystal clear about what's changing and when, and then give people time and space to adapt.
How to Communicate Change in Process
- Communicate a vision: One of the first steps for communicating change in the workplace is to communicate a vision for everyone in the department to understand. This vision could be a department that operates more efficiently or a department that uses safer methods of item transport.
- Explain changes in context for each role: After you communicate the vision, explain the changes within the context of each role. Change may affect some employees more than others, which is why it can be important to detail how these changes affect each individual role.
- Be transparent about intention: Being honest about your rationale can help employees better understand what they can do to help meet departmental goals and needs throughout the process.
- Describe steps of the change process: Next, describe a plan of steps that individual employees can take in the change process. Explaining each step can help team members learn their role and new actions.
- Provide Resources: After explaining the required changes, discuss what resources are available to employees to help them make these changes in their department or workstations.
- Allow employees/ stakeholders to give feedback: Before you initiate changes in the department, allow your employees to offer feedback. This can improve the process by sorting inefficiencies, correcting any productivity assumptions and reaching a better conclusion for each role in the department.
- Document change efforts: As your employees take steps in the change process of your department or company, document any efforts they make in real-time. This can track how well your employees received the instructions concerning the project. Document any changes to your product or service and try to determine whether it was circumstance or your instructions that caused the change.
- Gather feedback after the change: Once employees fully implement a change into a department, consider gathering feedback again after the employees evaluate the new system. Gathering continual feedback can help improve the current system by correcting any inefficiencies and promoting productivity.
- Seek continual improvement: It may be important to reassess and repeat the change process, depending on your departmental needs. Continuous improvement is important for a company and each of its departments so all team members can continue to work toward higher productivity goals and profitability.
Watch
Next, watch some videos explaining the concept of communicating change and progress.
Follow-Up and Follow-Through
Follow up with stakeholders to ensure that their feedback has been adequately addressed and that they are satisfied with the actions taken. Provide opportunities for ongoing dialogue and engagement to maintain momentum and continue improving the implementation of resource efficiency initiatives.
How do you follow up with stakeholders?
- Define your objectives: Before you reach out to your stakeholders, you need to have a clear idea of what you want to achieve from the follow-up. Do you want to confirm their understanding of your proposal, pitch, or report? Do you want to get their input on your recommendations, solutions, or plans? Do you want to ask for their support, endorsement, or referral? Having a specific and measurable objective will help you craft a relevant and concise message that aligns with your stakeholder's needs and expectations.
- Choose your channel: Depending on your objective, your relationship with your stakeholder, and their preferred communication style, you may choose different channels to follow up. For example, you may send an email to recap the main points of a meeting, a phone call to discuss feedback or questions, a video message to demonstrate a product or service, or a social media post to share a success story or testimonial. Whatever channel you use, make sure it is appropriate, accessible, and consistent with your brand and tone.
- Provide value: One of the key principles of thought leadership is to provide value to your audience. This means that your follow-up message should not be just a generic thank-you note or a reminder of your offer. Instead, it should offer something useful, relevant, and meaningful to your stakeholder. For example, you may share a resource, a tip, a case study, or a new insight that relates to their challenge, goal, or interest. You may also highlight the benefits, outcomes, or impact of your solution, idea, or project.
- Ask for feedback: Another way to provide value and engage your stakeholder is to ask for feedback. Feedback is essential for learning, improving, and adapting your thought leadership to your audience's needs and preferences. It also shows that you respect and value your stakeholder's opinion and perspective. When you ask for feedback, be specific, open, and constructive. For example, you may ask what they liked or disliked about your presentation, what questions or concerns they have, or what suggestions or recommendations they have for improvement.
- Follow through: The last step of following up with stakeholders is to follow through on your commitments, promises, or actions. This means that you should deliver what you said you would deliver, when you said you would deliver it. For example, if you agreed to send a proposal, a report, or a sample by a certain date, make sure you do so. If you received feedback, acknowledge it, thank your stakeholder, and explain how you will incorporate it or address it. Following through demonstrates your professionalism, credibility, and reliability as a thought leader.
Stakeholder Management
What is Stakeholder Management?
Stakeholder management is the process by which you organize, monitor and improve your relationships with your stakeholders.
It involves systematically identifying stakeholders; analyzing their needs and expectations; and planning and implementing various tasks to engage with them. A good stakeholder management process will be the means through which you are able to coordinate your interactions and asses the status and quality of your relationship with various stakeholders.
Why is Stakeholder Management important?
A vital part of running a successful project is to develop and maintain good relationships with those communities who will be affected and other stakeholders.
Investing time in identifying and prioritising stakeholders and assessing their interests provides a strong basis from which to build your stakeholder engagement strategy.
Benefits of Stakeholder Management
Companies that have grasped the importance of actively developing and sustaining relationship with the affected communities and other stakeholders are reaping the benefits of improved risk management, increased stakeholder support, and better outcomes on the ground.
Good stakeholder management also brings in ‘business intelligence’. Understanding stakeholder concerns and interests can lead to ideas for products or services that will address stakeholder needs; and allow the company to reduce costs and maximise value.
How to create a Stakeholder Management Plan
A Stakeholder Management Plan is a document that outlines appropriate management strategies to effectively engage stakeholders throughout the lifecycle of the project, based on the analysis of their needs, interests and potential impact on project success.
Be strategic and clear about whom you are engaging with and why, before jumping in. It not only helps save time and money, but also helps manage expectations and gain trust.
Stakeholder Management Plan in 5 Steps
Create a plan that outlines appropriate management strategies to effectively engage stakeholders throughout the lifecycle of the project.
Consultation Essentials
- Stakeholders Identification
- Who are your stake holders?
- What are their key groupings and sub-groupings?
- Remember - not all stakeholders in the same group will necessary have unified opinions or priorities.
- Stakeholder Analysis
- What are stakeholder group interests?
- How will they be affected, to what degree?
- What influence they could have?
- Any other information to help better understand their needs, priorities and issues?
- Strategy and Priority
- What are the strategic reasons to engage with stakeholders?
- What is the approach to each stakeholder group?
- What are your priority stakeholders? Why?
- What are the most appropriate ways to engage them?
- Responsibility
- Who is within the company responsible for what activities?
- Any overlapping of activities that present an opportunity for collaboration?
- Monitoring and Reporting
- How will the activities and results be captured, tracked, reported and disseminated?
- How and when to update the plan as the situation is dynamic and interests and priorities might change over time?
Questions to be asked before developing the plan:
What are the strategic reasons for consulting with stakeholders at this stage?
Who needs to be consulted?
What are the priority issues (for them and for you)?
What will be the most effective methods of communicating with stakeholders?
Who within the company is responsible for what activities?
Are there any other engagement activities that will occur in the proposed timeframe (perhaps with other sections of your organisation)?
Are there opportunities to collaborate to ensure key project messages are consistent and avoid consultation fatigue?
How will the results be captured, tracked, reported and disseminated?
Understanding your Stakeholders
The key to a successful stakeholder engagement or public consultation program is to start with a good understanding of your stakeholders. And make sure you are testing and refining that understanding throughout the process.
Learn and Iterate
Use feedback from stakeholders as a learning opportunity to continuously improve implementation processes and outcomes. Reflect on lessons learned, successes, and challenges encountered, and incorporate these insights into future initiatives and decision-making processes.
Acknowledge and Appreciate
Acknowledge and appreciate stakeholders for their contributions and feedback. Recognize their role in shaping the implementation of resource efficiency initiatives and express gratitude for their ongoing support and collaboration.
Watch
Watch this video giving some examples to acknowledge and show gratitude.
And this video from Mel Robins explains why showing appreciation is your superpower.
By actively seeking and acting on feedback from stakeholders, organizations can ensure that their resource efficiency initiatives are aligned with stakeholders' needs and priorities, leading to greater engagement, buy-in, and, ultimately, more successful outcomes.
