Meet Tracy Williams

This is Tracy Williams from ACE Finance.
In this module, you will learn the skills and knowledge that enable Tracy to perform the role of a Data Analyst, which involves knowing how to:
- determine the purpose and scope of big data analysis
- analyse initial trends and relationships in captured big data
- finalise big data analysis.
We will be following Tracy in the performance of these tasks. Before we begin, let us learn more about Tracy's role.
Tracy's role:
Tracy reports to the Chief Data Officer (CDO) as a Data Analyst at ACE Finance. Tracy's role is to analyse transactional and non-transactional big data to provide insights that enable the organisation to:
- identify trends and relationships within big data
- establish data acceptability
- form recommendations based on the analysis
- report on analysis findings.
Watch the following video to understand what is typically involved in the role of a data analyst.
Let us further explore big data analysis, by asking Tracy the following questions.
A popular definition for big data is:
Big data is high-volume, high-velocity and/or high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing that enable enhanced insight, decision making, and process automation. 1(Gartner 2022)
Every day, companies receive vast amounts of data from their multitude of interactions and processes. This massive amount of data is produced by different sources such as social media platforms, weblogs, Internet of Things (IoT) devices (e.g. sensors found in smart devices) and many more. Traditional database management systems cannot handle this vast amount of data.
Big data is much more than just large amounts of data. Five key characteristics make big data useful. When these characteristics are met, the large amounts of data yield the potential that is big data. These five characteristics are often referred to as the 5 Vs of big data.
- Volume - the amount of data large enough for the task at hand
- Velocity - quick data capture and analysis for timely business decisions
- Variety - related data from different data types and sources
- Veracity - reliable and trustworthy data
- Value – data analysis that provides value
It is challenging to understand and comprehend how ‘big’ big data really is, as the amount of data collected keeps growing exponentially each millisecond.
Watch the following video to understand big data and why we should understand where it comes from and why it is useful. Pay close attention to the difference between large amounts of data and what is called ‘big data’.
After watching the video answer the following questions.
Knowledge check
Complete the following three (3) tasks. Click the arrows to navigate between the tasks.
When analysing big data, analysts follow a process that includes multiple stages. At a high-level, the stages of big data analysis are as follows. 2
- Data requirement gathering – This is the first step in data analysis, and it is where we figure out what data we need and in what form.
- Data source identification and management – This is where we identify different sources of data, which can give us data in their required format and ensure that we can manage this data.
- Cleaning and processing of data – This is where we transform the data into a form that can be used directly in visualisations.
- Exploratory data analysis – This is where we explore the data available to us to figure out what exactly should be conveyed in the visualisations.
- Data communication – Finally, we will generate the charts, and graphs, combine them into reports and communicate them to stakeholders.
Watch the following video to learn more about big data analytics and what it involves.
After watching the video answer the following questions.
Knowledge check
Complete the following two (2) tasks. Click the arrows to navigate between the tasks.
The value of big data lies in our ability to extract insights and make better decisions 3(Rappa 2012)
Big data plays a vital role in enabling businesses to make informed decisions. With recent technological improvements, harvesting and processing large volumes of data is now economical. Combining this with accurate analytics can yield a significant competitive advantage.
Businesses may perform big data analytics for many different reasons to gain an advantage. These include:
- Exploration of new revenue opportunities
- Improve operating efficiency
- Improve marketing effectiveness
- Build stronger customer relationships
- Identification of business risks.
Businesses need to be aware of some aspects of big data analytics. Poor data and substandard analytics will lead to potentially detrimental decisions. Organisations must also comply with various data protection and privacy laws and regulations.
Knowledge check

Big data analytics can assist business decision-making across different business settings.
Watch the following videos to understand how different industry sectors can benefit from big data analytics.
Big data analytics in the retail industry
The retail industry benefits significantly from big data analytics. Watch this video to learn how.
Knowledge check
Big data analytics in marketing
Big data analytics are commonly used for marketing purposes. Watch this video to learn more.
Knowledge check
Big data analytics in the financial services industry
Big data provides many benefits to the finance industry. Watch the following video about big data for financial services
Knowledge check
Big data analytics in business auditing
An interesting use of big data analytics is in business auditing. Watch this video to learn more.
Knowledge check
Big data analytics in research and development
Research and development activities often rely on big data analytics. Watch this video to learn about one example.
Knowledge check
Big data analytics in healthcare
Healthcare decisions can be significantly improved by utilising big data analytics. Watch this video to learn more.
Knowledge check
A wide variety of tools and technology platforms are available to analyse big data. Each tool or platform will have different capabilities for extracting, transforming and analysing data.
Typically, the choice of these tools and platforms may differ from organisation to organisation. Some big data analytics tools may have additional and more advanced tools and features that suit a particular requirement. If your organisation prefers to use a specific tool or platform, you must become familiar with it and learn how to use it effectively.
However, for the purpose of analysing big data, the selected tool or platform should have the functionality to:
- obtain data from a variety of big data sources
- import data into a common platform for processing
- perform transformations to the data
- explore statistical summaries of the data
- categorise and group data for analysis
- detect errors or inconsistencies in the data
- perform a variety of data visualisations to derive insights.
Watch this video that shows examples of some commonly used analytics tools and technology platforms.
The following outlines some examples of the tools and platforms used for big data analysis, which are categorised based on their main functional capabilities.
- Tools for data extraction, transformation and loading (ETL)
(Capturing data, performing validations and testing)
- Visualisation
(Reporting, analytics, dashboards and KPIs)
- Platforms
(Storage and processing big data sources)
Platforms
A big data platform is more than a repository for data.
A data platform is a complete solution for ingesting, processing, analyzing and presenting the data generated by the systems, processes and infrastructures of the modern digital organization. 5(Splunk 2022)
Watch this video to learn more about the functions of big data platforms
Other platforms with different offerings are summarised at this Built In page What is a Data Platform?
Reporting and Business Intelligence (BI) tools
A crucial part of business analytics is the reporting mechanism. Reporting needs to be organised to readily show key performance figures and provide data to facilitate decision-making. The design of the reporting system needs to respond to the business requirements carefully and may include any of the following:
- Static reports showing a snapshot in time
- Real-time dashboards showing key performance
- Interactive dashboards allow exploration of data
- Visualisation of key trends and patterns
- Adaptations for mobile access
Regardless of the reporting mechanism, useful information needs to be provided in a timely and easy-to-understand manner.
Dashboards
Dashboards are designed to share key business analytic parameters and display them as tables, charts, graphs, timelines, etc., depending on the data type. A dashboard may have some interactivity to show different details but will generally not offer explanations of contributing factors.
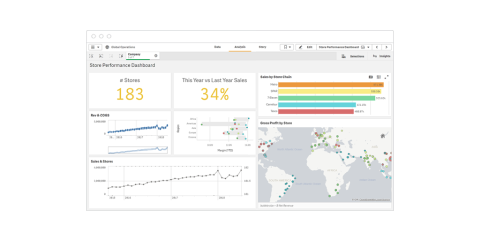
The following example explores the performance of retail chain stores. Note the clear display of performance indicators and comparison information that should be close to real-time.
Interactive visualisations
Dashboards may also provide some interactivity, such as allowing the choice of time period or a particular business entity. The dashboard can update the visual representation of the data to match the selection.
Explore the following demonstration that shows how an interactive dashboard can display data. Here a user can select different time frames, customers or product types. Observe how the visualisation changes in response to the interactions.
View the demonstration here.
Reporting
Traditionally, reporting was in the form of a printed document providing a quarterly or monthly summary of performance and indicators.
Analysis results can also be presented as an online interactive report, providing a narrative with supporting visualisations. The interactivity generally provides additional detail rather than responding to a query.
An example can be seen at this infogram website. Note that this report is a snapshot of sales performance for a particular month, but the website does offer some interactivity if the user requires further detail.
Automation tools
One of the critical requirements for big data analysis to provide timely reports is to use technology to automate data collation and preparation.
Significant advances in computer processing speeds and the reduced cost of data storage have allowed big data analytics to become far more widespread across many different applications.
Watch the following video introducing Automated Data Analysis (ADA).
The use of automation tools can help fast-track the big data analysis process to get results more quickly, handle more data, save costs and increase productivity.
Automation tools have the ability to:
- capture data automatically from required data sources
- analyse time-series big data to detect anomalies and patterns automatically
- prepare data by categorising them according to specifications outlined
- create data models automatically
- provide insights into the data in real-time
- automate the repetitive processes to increase productivity further and cater for increasing demands.
Some examples of Automation tools used for big data analysis are, but not limited to the following:
- SAS Forecasting for the New Era
- Add AI to Your BI Stack
- Getting Started with Hevo - An Overview
- Alteryx Explained
Knowledge check
After you have watched the video about ADA, read the following statement and decide whether it is True or False.
The role of technology
The rapid advancement in technology allows us to:
- generate large volumes of ever-increasing forms of data (due to increased use of IoT, wearables, sensors, various other sources etc.)
- store more data using scalable cloud storage solutions
- analyse, process and turn raw data into valuable information.
Watch the following video to understand the role of technology in data analytics. Pay attention to the various technologies mentioned throughout the video.
Knowledge check
Some of the popular technologies used in big data analysis are as follows.
Cloud technology
Cloud platforms have built-in tools and features to analyse and process big data that can easily connect with big datasets stored in the cloud. They also allow for quick analysis and generation of reports and facilitate sharing these reports with stakeholders.
Machine Learning
Once data has been cleaned and processed, links between the initial conditions and the outcome can be investigated. Machine learning can be applied to make this process more wide-ranging and rigorous. Analysing historical data can help understand the relationships so representative models or algorithms can be built. If a new question or situation is envisioned, the model can be used to predict the likely outcome.
This video shows various steps taken when building a Machine Learning Model.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the term applied to the programs that replicate human thinking. This includes learning from historical events to solve problems and make predictions. Machine learning is a subset of AI.
Watch this video to learn about various AI trends for 2024.
Topic summary
Congratulations on completing your learning for this topic Business in Action – Analysing big data.
In this topic you have learnt the following fundamental concepts behind analysing big data.
- Purpose and benefits to organisations of big data analysis
- The stages of big data analysis
- Common tools to analyse big data including business intelligence (BI) tools
- Technology platforms to analyse big data
- The role of technology and automation tools in performing big data analytics.
Check your learning
The final activity for this topic is a set of questions that will help you prepare for your formal assessment.
Knowledge check
Complete the following six (6) tasks. Click the arrows to navigate between the tasks.

