Welcome to the Indicators of Positive and Negative Wellbeing topic.
This is the first topic of our Wellbeing Responsibilities module.
The learning outcome of this module is to identify indicators of negative wellbeing to promote and support the mental and physical welfare of a construction team following statutory provisions and employer responsibilities.
Click ‘Video Transcript’ or the plus icon (+) to expand and reveal the transcript for the previous video.
Welcome to this module on Wellbeing Responsibilities.
The learning outcome of this module is to identify indicators of negative wellbeing and to promote and support the mental and physical welfare of a construction team in accordance with statutory provisions and employer responsibilities. You will look at identifying indicators of negative wellbeing, the application of statutory provisions and employer responsibilities, and workplace considerations to indicators of a change in mental health. So, let's dive into it.
Construction work often involves hard physical labour, long days and working outside in extremes of temperature.Live-Work New Zealand
Working in construction can be challenging for both the body and mind. However, there are wellbeing habits and routines that could help get you and your team be prepared for any challenges that come your way.
Your staff's health affects the project build, and the project build affects the health of your team. ensuring the wellbeing of staff is crucial for creating a positive and productive work environment.
At the very core, employee desires:
- to be acknowledged as an individual
- to be recognised for the job they do
- to grow, learn and feel that they contribute to the wider team.
A big part of achieving the employee's desires can be done through having a balanced and healthy sense of wellbeing.
Wellbeing
Wellbeing means having the capacity to comfortably be who we are.
In its widest sense, wellbeing refers to a person’s level of good physical and mental health and the extent to which they can live healthy and flourishing lives. A person with a healthy level of wellbeing can cope with life's stresses and contribute to their community.
As a construction supervisor, you are overseeing the wellbeing of your team in general. Although you are not monitoring every single decision that your team members are making, it is important that you set the bar for yourself first.
Knowing what works well for you to achieve that steady sense of wellbeing could help you when it comes to assisting struggling team members.
Reflection
Reflecting on where you are today. Rate your sense of wellbeing on a scale of one to ten, with one to indicate feeling burnout and ten to indicate feeling great and thriving.
Now that you have reflected on your own level of wellbeing. Describe to yourself what a perfect day would be for you. Using the following Documentation Tool, use the prompts on the left and fill out your answers. There are no right or wrong answers. This is merely a visualisation tool to help imagine what a perfect day would be.
Indicators of Positive Wellbeing (Physiological)
Let’s look at each of the indicators that are affecting our physiological or physical body first. Our body is a vessel that carries us through life. Looking after it should be our first priority and you can see the flow on effect on other parts of your life.
EXPLORE
Watch: I Did My Best Though (20 seconds)
The following short animation meme is a fun take on looking into the causes of why you might be feeling down.
Sign one: Eating habits and fluid intake
Eating and hydrating your body well need not be complicated.
Make sure your lunch includes your favourite takeaway or home-packed meals. Aim for a good balance of protein, carbohydrates, and fibre to keep you full and energised throughout the day. Check your fluid intake by asking yourself, "Have I been drinking enough water today?" Healthinfo New Zealand recommends at least 8 cups of water a day. Lastly, pay attention to your bowel movements.
You know your body best, so watch for any signs and adjust your diet.
Explore
Try a new lunchbox combo this week. Go to one of these recommended links to review some of their eating well tips and healthy lunch ideas:
Sign two: Sleeping
Everything in moderation is a good guideline with many aspects of wellbeing, including the hours of sleep you need each night.
Too little sleep gets you feeling tired the next day, and too much sleep can throw you out of your circadian rhythm (natural sleep-wake cycle). Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day can build a good sleep pattern.
Even when you think you have things under control, normal sleep patterns can also be thrown out of whack with disruptions caused by the following:
- worrying and overthinking
- overeating or too much caffeine
- binge-scrolling or binge-watching on your device.
The previous are just a few examples of sleep disruptors; you might find unique examples of your own.
Night mode on your phone
Prolonged exposure to blue light from your device mimics the daylight temperature and tricks your mind into thinking it's still daytime when it's actually nighttime outside. If you have not scheduled your device into a night mode try to do so and see if it makes a difference to your night routine.
Sign three: Movements
Unlike sedentary desk jobs where it’s common to sit all day. Construction supervisors have the opportunity to move their bodies actively throughout the day.
Walking around sites to do inspections, driving from the office to the site to the supply store, there are plenty of opportunities to increase the step count in your day.
When supervising your team members, ensure they’ve enough variety in their tasks throughout the day to avoid repetitive strain injury. Also, ensure safety equipment and scaffolding are installed safely to prevent falls and avoid bodily harm.
Sign four: Social activity
The nature of work on a construction site combines individual and teamwork.
Once team members know what they need to do, they’d be off to complete their tasks individually. Depending on the noise level, team members could be isolating themselves using ear mufflers or putting on their AirPods (or wireless headphones) to listen to music or audiobooks.
Use breaks and meal time to reconnect with team members and encourage friendly banters. Organise optional social gatherings outside of work to allow opportunities for team members to know everyone else outside the work capacity.
Explore
What do you currently like to hear while you’re driving?
Is there a Spotify list you like to listen to? or is there an audiobook you enjoy?
Sign five: Device use
Electronic devices such as laptops, tablets and smartphones are game changers.
With smartphones in particular, our modern lives have relied so much on them. Communication can be done instantly, and we also have mini-computers in our pockets to help get our job done quickly. There are also endless options for entertainment to fill those idle minutes, from short videos, to games and even watching full-length movies.
However, with smartphones' conveniences, there are also downsides to it. Popular smartphone applications have been likened to gambling machines. The algorithm designed to run these apps can get you really sucked in and trapped you into mindless scrolling or passive use. There are also the dangers of feeding your unconscious bias and exposing yourself to unwarranted information or marketing.
Be mindful of your device use and use it to your advantage. Keep track of the time you consume and assess if it is really time worth spending. Just like any other type of addiction, notice the signs when device use starts to eat up important chunks of your time. Taper use and find other replacement activities that could still bring you that joy or dopamine kick.
Sign five: Dignity
On-site practices of dignity involve treating workers with respect, fairness, and consideration for their rights as human beings. This means creating a work environment where workers are valued, their contributions are recognised, and they are treated with decency and empathy.
It includes providing fair wages, ensuring equal opportunities, and fostering a culture of inclusivity and respect regardless of race, gender, age, health, or other personal characteristics. Additionally, dignity means protecting workers from harassment or any form of discrimination.
Mental Wellbeing (Psychological)
In addition to the previous list of things that affect our physical health, our mental wellbeing is also influenced by a range of things, including:
- our genetics
- life experiences
- the choices we make
- the environments we live and work in
- the actions we take and the way we think.
Team members who are consistent with their wellbeing practices can be considered to be thriving and excelling in their personal and work lives.
Here are further indicators of thriving and excelling individuals:
Excelling
- cheerful and joyful
- solution-focused
- energetic
- high-job performance
- prioritise sleep and recovery
- flow - intense engagement
- fully realising potential
- actively seeking connection
Thriving
- normal mood, some variations
- positive
- calm
- function normally in a job
- sleeping well
- focused
- eating normally
- normal social activity
Both physiological and psychological indicators contribute to the fluctuations we experience in our wellbeing, and it's important to keep in mind that No one can be 100% every day.
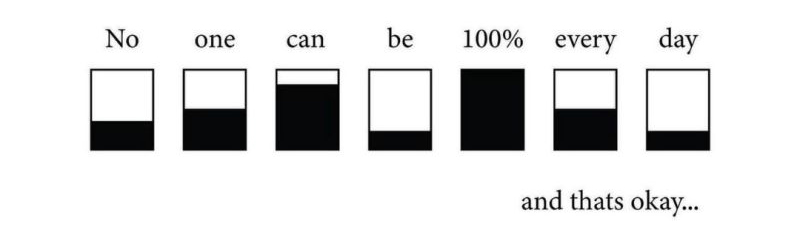
Image by Strength Visuals on Instagram
Explore
Find your wellbeing hero and a wellbeing quote that resonates with you. Here's one to start with from a spiritual leader in India, Sadhguru:

Trigger Warning
The following topic contains issues such as violence, self-harm, and drug, alcohol and substance abuse.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
In the previous topic, we looked at positive wellbeing indicators in individuals.
Next, we look at a well-known framework called Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs to help us understand negative wellbeing indicators.
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a great tool for understanding what makes us feel good and function well.
Created by Abraham Maslow, a renowned psychologist, this framework breaks down human needs into five levels:
- basic physical needs
- safety
- love and belonging
- esteem
- self-actualisation.
The pyramid shows us that we need to meet our basic needs before we can focus on higher-level ones. Using this model, we can better understand what contributes to our wellbeing and create environments supporting personal growth and happiness.
EXPLORE
Watch: Maslow's Mistake (01:11 minutes )
Let's listen to what a prominent thought leader, Simon Sinek has to say on the theory's flaws.
How can you tell if a team member is struggling?
There isn't one particular telltale sign of struggle.
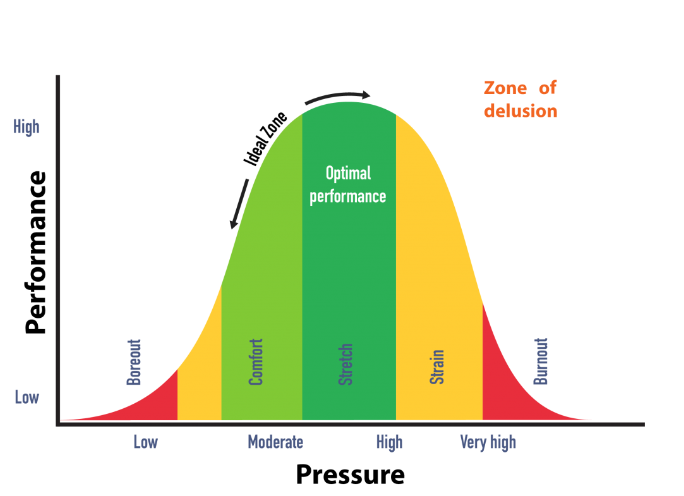
However, the onset of pressure can be a determining trigger. So, how do pressure, performance and stress relate to one another?
| Pressure | Stress (Strain or Burnout) |
| A healthy level of pressure keeps us motivated and productive. | An accumulation of unaddressed pressure could create overwhelming demand and lower performance. |
Here are some indicators of struggle, starting with burnout.
Sign one: Burnout
We looked at how an accumulation of pressure can cause burnout. Employee burnout could manifest itself in physical, mental, and emotional exhaustion.
Team members often face demanding work schedules, tight deadlines, and physically challenging tasks, which can contribute to burnout if not managed properly. Burnout can have serious consequences on the individual's and wider team's health and safety, as well as the overall success of the building project.
Here's a curved diagram from Delphis Learning to help illustrate how overwhelming pressure could lead to burnout.
Sign two: Absenteeism
One of the ways you can tell when a team member is struggling is through the obvious indicator of absenteeism or not showing up.
In New Zealand, a full-time employee is entitled to four weeks of annual leave each year when they have worked for their employer for 12 months. They are also entitled to ten days of sick leave, depending on how long they have worked for the same employer and their entitlement date.
It is human nature to fall sick, care for a sick loved one, take time off for holidays, or any other personal reasons. However, it is important that your team members keep that line of communication with you and keep you in the loop about upcoming leave. It is unacceptable to skip a day at work and not inform anyone about it. Ensure new staff members are aware of what they need to do should they wish to take a sick or any other type of leave.
The following diagram illustrates how both absenteeism and presenteeism affect work productivity.
Sign three: Presenteeism
Presenteeism is when employees come to work despite being unwell, leading to reduced productivity and potentially spreading illness to others.
Being present at work while showing indicators of struggle or negative wellbeing could further aggravate their problem and have a spillover effect on the work environment.
explore
Watch: Mates in Construction: Concentrating (01:11 minutes)
The following video from Mates in Construction, looks at how to look for one of the signs of struggle and starting a conversation.
Sign four: Aggression
Signs of onsite aggression by teammates can manifest themselves in many ways.
It may be overt, such as yelling or physical aggression, or more subtle, such as over-protecting, over-controlling or being passive-aggressive.
Aggression of any sort can be directed at specific people or groups, or it can be generalised hostility. No matter how it appears, workplace aggression poses a significant concern that can adversely affect morale, productivity, and safety. If not addressed, it may escalate to violence and even result in incidents of harassment or assault.
Sign five: Anxiety
In the construction industry, workplace frustration may arise from irritation, outrage, or a sense of unfairness during their daily duties.
This could prompt employees to adopt a forceful approach to address issues. And can then manifest itself in actions that are more destructive than required, potentially worsening the situation rather than resolving it.
Therefore, recognising these individual signs is imperative. Potential signs could include:
- increased tension and hostility
- disruptive behaviour
- frequent arguments
- frequent complaints
- claims of sabotage
- destruction of property
- increased safety violations.
Understanding the triggers can be the first step to preventing full-on emotional outbursts by your employees.
On your site projects, your employees might require support in recognising the factors that provoke their emotions. Training sessions urge your team to discover methods for managing or diffusing their frustration while maintaining a professional demeanour.
This could involve acknowledging their emotions without criticism or attempting to resolve disagreement through mediation.
Sign six: Irritability, sadness and hopelessness

In a construction site, when these signs are observed in conjunction with other indicators, it suggests that an individual may be struggling significantly with their mental health.
Persistent sadness can be a particularly concerning sign, as it often indicates deeper emotional distress. This persistent sadness, coupled with irritability and a sense of hopelessness, can affect their ability to perform tasks safely and effectively.
They might show physical signs of distress, like crying or looking upset. Spotting these signs early and offering support is key.
Sign seven: Withdrawal
Humans are social beings, and social connections play a role in wellbeing.
When an individual starts withdrawing from colleagues, it may suggest a decline in their mental wellness. Social isolation can contribute to feelings of loneliness, stress, and anxiety, which can negatively impact both mental and physical wellbeing. If someone is experiencing high levels of stress, burnout, or feeling overwhelmed, they may resort to isolating themselves as a way to deal with these emotions going around their head.
Sign eight: Negative risk-taking
Negative risk-taking can jeopardise the wellbeing of individuals and other project site members; examples of this behaviour may look like this:
- job carelessness
- site recklessness
- ignoring safety protocols
- creating unmanageable workloads for themselves or others
- setting unrealistic deadlines
- disregarding personal mental health issues
- creating a hostile work environment.
Spotting these negative risk-taking behaviours early onsite will help reduce the risk of loss of life due to the hazardous nature of worksites. Elements of job carelessness or site recklessness can be spotted with regular assessments, safety audits, and staff feedback, promoting a safer and healthier work environment for all.
Sign nine: Lack of participation
When a team member is struggling, they might be lacking in participation and have difficulties communicating. They might be:
- Avoiding conversations or participation in meetings.
- Having difficulty expressing their thoughts or ideas clearly.
- Showing minimal facial cues and verbal communication.
Sign ten: Cigarette, alcohol and substance use
Recreational use of cigarettes, alcohol and substances can turn into abuse. If you are worried about the level of use and how it affects you and those around you. Reach out for help - Alcohol and Drug Helpline.
Explore
There has been numerous research done in New Zealand to address cigarette, alcohol and substance use. Here are a few external links for you to explore:
- Infographics on key facts about drinking in New Zealand.
- Patrick Gower's article and documentary on vaping.
- Patrick Gower's article and documentary on booze.
- Patrick Gower's article and documentary on 'all drugs'.
- Build Magazine's article Cracking down on drink and drugs.
According to The Mental Health Matters “Re-Mind” website, individuals' wellbeing exists on a spectrum of categories as follows:
| In Crisis | Struggling | Unsettled | Thriving | Excelling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
very anxious very low mood absenteeism exhausted sickness, physical pains isolation very poor sleep weight loss psychotic breakdown severe drug, alcohol, and substance abuse |
anxious sad and depressed low self-esteem tired poor work performance presenteeism poor concentration poor sleep poor appetite drug, alcohol, and substance abuse |
worried nervous, edgy irritable, frustrated self-doubting gloomy and sad trouble sleeping tired distracted decreased social activity |
positive calm normal mood, some variations function normally in a job sleeping well focused eating normally normal social activity |
cheerful joyful solution-focused energetic high-job performance prioritise sleep and recovery flow - intense engagement fully realising potential actively seeking connection |
Thriving and Excelling
These two categories fall into the green zone.
Individuals in these categories have healthy coping mechanisms and the ability to be flexible.
They're resilient towards life challenges and can apply problem-solving skills accordingly. They're also able to self-regulate their emotions and self-soothe to provide comfort in times of distress.
Unsettled and Struggling
These two categories fall into the amber zone.
Individuals in these categories have trouble maintaining a sense of balance in their personal lives.
They're often feeling anxious or overwhelmed by daily responsibilities. They're also likely to experience mood swings and may have difficulty maintaining a positive outlook on life.
In Crisis
This category falls in the red zone.
Individuals in this category are facing severe personal challenges that significantly impact their wellbeing.
They're often experiencing intense stress, anxiety, or depression. They may struggle with feelings of hopelessness or helplessness, and their ability to cope with daily life is severely compromised. These individuals might also exhibit signs of extreme emotional distress, such as lashing in anger, withdrawal from social interactions, or an inability to focus on even the simplest tasks. Immediate support and intervention are crucial for those in this zone.
Initiating conversation
The following steps can help ensure successful conversations where the needs of both team members and employers are considered:
| Before you approach the person. |
Ask yourself:
|
|---|---|
| Where and when? |
Keep it casual. Find quiet opportunities to catch up before, during or after work. Choose a location where they feel comfortable enough to open up. If you have built rapport, taking them offsite is a good idea, such as going for a walk around the block or grabbing a coffee. Choose a spot away from others and quiet enough to talk comfortably. |
| Ways to start the conversation. |
Don't worry if you don't quite know what to say. By being supportive and listening, you're helping make a difference. |
| Help them open up by asking questions. |
|
| Mention specific things that have made you concerned for them. |
If issues impact their productivity, think about structuring your talk by highlighting the good things they have achieved and addressing a particular concern. Always nip it in the bud before it becomes a bigger problem. |
| What if the person doesn't want to talk? |
Be relaxed if the discussion doesn't go as you'd hoped. If the person doesn't want to speak about it, respect their choice but leave the door open for further dialogue. |
Adapted from Mental Health in Construction.
Workplace Considerations
Starting a conversation about mental health among the team has been shown to lead to collective positivity, including:
- better physical health
- reduced absenteeism
- reduced presenteeism
- lower staff turnover
- improved work performance, motivation, commitment and energy
- less tension and conflict, more connectedness, kindness, tolerance and patience.
A positive or mentally thriving workplace environment can help people going through stress or any personal factors outside of work.
However, having a poor workplace understanding of mental health can make situations worse.
As we work in teams on site, we can all take a role in managing each other’s wellbeing by having conversations and having them early enough so that they matter.
EXPLORE
Watch: The most important lesson from 83,000 brain scans (14:36 minutes)
The science behind mental health and what brain scans show about brain health.
