| Day One | Day Two | |
|---|---|---|
| Course Content | AC generation - principles & operation. | AC resistance and impedance. |
| Self-directed Learning | Complete and submit any outstanding assessment work. |
Complete and submit any outstanding assessment work. |
In order for you to gain the most value from your qualification and to prepare you for your assessment and the industry, make sure you complete all of the online and SDL tasks.
What we're covering:
- varying the magnetic field
- slip rings
- sine waves
Begin this topic by reading about Electric Circuits on pages 1-3 at the BBC Bitesize site.
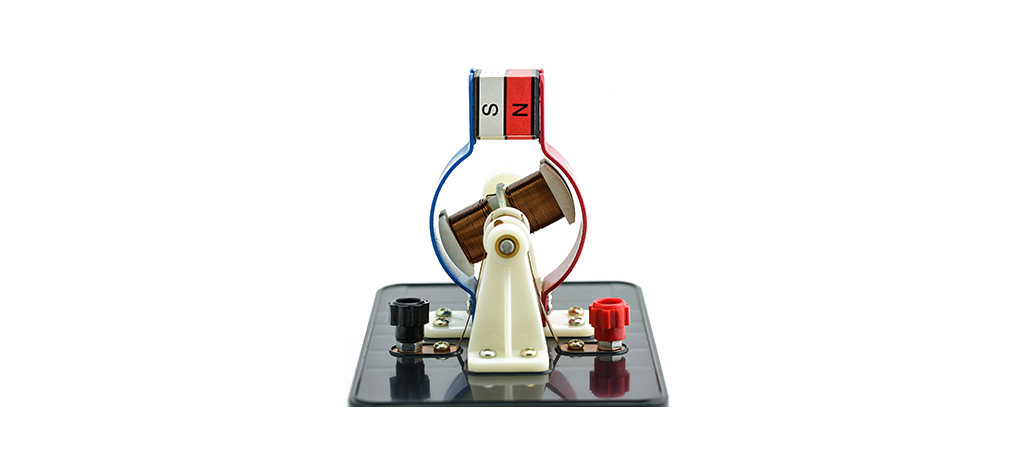
AC or DC generators apply the same principle to generate electric current - current will be induced in a conductor inside a magnetic field when there is a relative motion between the conductor and electric field.
There are two ways to vary the magnetic field acting on the conductors - either by rotating the magnetic field around a stationary conductor or spinning the conductor inside a stationary magnetic field. In both cases, an electric current is induced in the conductor.
The AC generator is designed to generate alternating current with a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz. The current induced in the armature is supplied to the circuit using slip rings.
The slip rings are two separate conducting rings connected to each terminal of the armature. They maintain constant contact with the same sides of the coil.
Slip rings supply current to the circuit through a sliding contact called brushes. If we connect two terminals of an external load with these two brushes, we will get an alternating current in the load. Brushes make continuous contact between the external circuit and the slip rings.
Note - the rings always rotate with the armature while the brushes remain stationary.
This video gives a very straightforward explanation of the working principle of AC generator. Watch it a couple of times if necessary to ensure you fully understand the mechanism. Working Principle of AC Generator
Developing the Sine Wave
As the armature rotates, each half cuts across the magnetic lines of force at the same speed. Thus, the strength of the voltage induced in one side of the armature is always the same as the strength of the voltage induced in the other side of the armature. Each half of the armature cuts the magnetic lines of force in a different direction. For example, as the armature rotates in the clockwise direction, the lower half of the coil cuts the magnetic lines of force from the bottom up to the left, while the top half of the coil cuts the magnetic lines of force from the top down to the right. Therefore, the voltage induced in one side of the coil is opposite to the voltage induced in the other side of the coil. The voltage in the lower half of the coil enables current to flow in one direction, and the voltage in the upper half enables current to flow in the opposite direction.
However, since the two halves of the coil are connected in a closed loop, the voltages add to each other. The result is that the total voltage of a full rotation of the armature is twice the voltage of each coil half. This total voltage is obtained at the brushes connected to the slip rings and may be applied to an external circuit.
This diagram shows four different positions of the coil in a simple AC generator, and the potential difference produced at each position.
Self-directed Learning
Look at the glossary page in the menu and download the worksheet. You should make sure you know the words listed in the glossary.
Complete and submit any outstanding assessment work.

What we're covering:
- impedance, capacitance and inductance
In a DC circuit the opposition to current flow is called resistance (R) and measured in ohms, Ω.
In an AC circuit, we talk about impedance (symbol Z) which is a combination of both resistance and reactance. Impedance is similar to resistance, but it also takes capacitance and inductance into account.
• Resistance (R) is the slowing of current due to effects of the material and shape of the component. This effect is largest in resistors, but all components have some resistance.
• Reactance (X) is the slowing of current due to electric and magnetic fields opposing changes in the current or voltage. This is most significant for capacitators and inductors.
The magnitude of the impedance Z of a circuit is equal to the maximum value of the potential difference, or voltage, V (in volts) across the circuit, divided by the maximum value of the current I (measured in amperes) through the circuit, or simply:
Impedance is measured in ohms, Ω.
Simple AC circuits involving nothing more than an AC power source and resistance, obey the same simple laws and rules as DC circuits. However, AC circuit measurements and calculations become very complicated when we factor in inductance and capacitance.
Measurements of AC voltage and current must be expressed in the same terms (peak, peak-to-peak, average, or RMS). For instance, if the source voltage is given in peak AC volts, then all currents and voltages subsequently calculated must also use peak units, but if the source voltage is given in AC RMS volts, then all calculated currents and voltages should also be in AC RMS units. This holds true for any calculation based on Ohm’s Laws, Kirchhoff’s Laws, etc.
Unless otherwise stated, all values of voltage and current in AC circuits are generally assumed to be RMS rather than peak, average, or peak-to-peak.
This video looks at what happens when a coil is connected to a DC supply and then to an AC supply.
AC Theory: The Mystery of the Coil
Exercise 24
When you have completed the questions below, email or message your tutor to find out how well you did.
- In this AC circuit, the resistor offers 300 Ω of resistance and the inductor offers 400 Ω of reactance. Together their series opposition to alternating current results in a current of 10 mA from the 5 V source.
How many ohms of opposition does the series combination of resistor and inductor offer?
What name do we give this quantity? What is its symbol? - In this AC circuit, the resistor offers 3 kΩ of resistance and the capacitor offers 4 kΩ of reactance. Together their series opposition to alternating current results in a current of 1 mA from the 5 V source.
How many ohms of opposition does the series combination of resistor and capacitor offer?
What name do we give this quantity? What is its symbol? - With reference to the circuit shown answer the following questions:
- What is the reactance XL of inductor L?
- What is the circuit impedance Z?
- What is the supply Current IS?
- What is the voltage VR across the resistor R?
Self-Directed Learning
Look at the glossary page in the menu and download the worksheet. You should make sure you know the words listed in the glossary.
Complete and submit any outstanding assessment work.
Glossary
The following worksheet contains a list of words taken from this resource. To help improve your understanding, research their meanings or find the definitions in the workbook. There is space to write the definitions. You could also look up how to say the word – most online dictionaries will demonstrate this.
Course 3 Reference List:
- alexgeekcouk. (2010, November 18). Transformer Animation. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/VucsoEhB0NA
- Algebra Basics. (2015, May 23). Solving Basic Equations – Part 1. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/l3XzepN03KQ
- Algebra Basics. (2015, May 23). Solving Basic Equations – Part 2. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/Qyd_v3DGzTM
- Algebra Basics. (2015, May 23). What Is Algebra? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/NybHckSEQBI
- BBC Bitesize. (n.d.) Conductors and insulators. https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z48gmfr/test
- BCHydro - Powersmart for Schools. ( n.d.) Ohm's Law Explained. https://vimeo.com/560047171/9c76398224
- Beaty, W. (2007, November 8). Simple generator: AC electric generator for science fair. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/k7Sz8oT8ou0
- Brain, M. & Hall-Geisler, K. (2021, October 5). How Electric Motors Work. How Stuff Works. https://electronics.howstuffworks.com/motor.htm
- Brain, M. & Pollette, C. (2021, September 7). How Electromagnets Motors Work. How Stuff Works. https://science.howstuffworks.com/electromagnet.htm
- Brennan, E. (2021, October 21). How to Use a Multimeter to Measure Voltage, Current and Resistance. https://medium.com/eugenes-diy-den/how-to-use-a-multimeter-to-measure-voltage-current-and-resistance-962bb2931799
- Casio Calculator Tutorial. (2015, February 20).Overview of Essential Buttons (fx-83GT PLUS, fx-85GT PLUS, fx-300ES). [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/rn-XjUVJtyw
- CHMnanoed. (2010, January 16). Magnetism: Motors and Generators. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/d_aTC0iKO68
- Chrvoje engineering. (2020, June 20). Working Principle of AC Generator! [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/YkHhFho6L2Y
- CK-12 Interactives. (n.d.) Transformer simulation. https://interactives.ck12.org/simulations/physics/ac-transformer/app/index.html?screen=sandbox&hash=f0b5086c59b6e55620f0b4dee95ba2bb&source=ck12&artifactID=1916732
- CK-12. (2017, September 27). Generating and Using Electricity. https://www.ck12.org/section/generating-and-using-electricity/
- Csanyi, E. (2016, August 15). Basic Measuring of resistance, voltage and current using digital multimeter. https://electrical-engineering-portal.com/measuring-resistance-voltage-current-digital-multimeter
- Cyberphysics.co.uk. (n.d.) KS3: Magnetism Questions. https://www.cyberphysics.co.uk/Q&A/KS3/magnetism/A3.html
- Don’t Memorise. (2018, October 23). Physics: Magnetic Force and Magnetic Field. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/R4ht2RcWVlI
- Don’t Memorise. (2018, September 12). Electricity and Circuits: How does an Electric Bell work? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/nygn7wB7658
- Eaton Videos. (2020, July 22). Power Generation. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/ZSCEfJ4TXW4
- Electrical Technology. (2012). Difference Between AC and DC Generator. https://www.electricaltechnology.org/2020/06/difference-between-ac-dc-generator.html
- Electrical Technology. (2021). Basic Electrical Engineering Formulas and Equations. https://www.electricaltechnology.org/2020/10/electrical-engineering-formulas.html
- Electrical4U. (2020, October, 28). Working Principle of Alternator. https://www.electrical4u.com/working-principle-of-alternator/
- Electronics Tutorials. (2010, November 5). [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/tM5js2g1_HY
- Electronics tutorials. AC Waveform and AC Circuit Theory. https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/accircuits/ac-waveform.html
- Energy Education. (n.d.) Energy vs power. https://energyeducation.ca/encyclopedia/Energy_vs_power
- Flexbooks. (2019, May 30). CK-12 Physical Science for Middle School. Electromagnetic Devices. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-middle-school-physical-science-flexbook-2.0/section/22.5/primary/lesson/electromagnetic-devices-ms-ps/#x-ck12-TVNfUFMtTW90b
- FuseSchool – Global Education. (2020, August 10). Physics: Magnetism. Field Lines. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/SCnGfE7qxHc
- GCSE Physics. (2020, April 5). Electricity. Conventional Current VS Electron Flow. https://youtu.be/T7GfoBimQ3A
- GGHS Chemistry. (2018, February 3). How to use your calculator for scientific notation. Unit 8: General How-to Videos for Significant Figures, Scientific Notation and Rounding. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/FyZBLnp4_SI
- Iken Edu. (2016, March 22). Secondary Science: What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/3HyORmBip-w
- Instrumentation & Control. (2021, January 5). What Is OHMS Law ? [Explained in Under 5 Minutes]. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/uZ-m91IEkjQ
- Instrumentationtools.com. (n.d.) Developing a Sine Wave. https://instrumentationtools.com/wpcontent/uploads/2018/07/Developing-a-Sine-Wave-Voltage-of-Motor.png?ezimgfmt=ng:webp/ngcb2
- IOP - Institute of Physics. (n.d.) Magnetism & electromagnetism PPT.
- Jia, D. (2022, August 27). How to Use a Calculator. https://www.wikihow.com/Use-a-Calculator
- Joe Robinson Training. (2019, October 4). What is Electricity? Part 3: Which Way Do Electrons Flow? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/9p7XUAcdXIY
- Joe Robinson Training. (2020, February 19). AC Theory: The Mystery of the Coil. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/LXpXDga-7xM
- Joe Robinson Training. (2020, March 18). How to Calculate Power in an Electrical Circuit, Where Does the Power Formula Come From? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/xqanURIKnng
- Joe Robinson Training. (2020, March 18). How to Find the Power Formula Number 2 for Electrical Circuits, Calculating Power Without Voltage. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/lPfu-QpFnS8
- Joe Robinson Training. (2020, March 25). How to Find the Power Formula Number 3 for Electrical Circuits, Calculating Power Without Current. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/VX1P957sbGU
- Joe Robinson Training. (2020, March 8). How to Calculate Power in an Electrical Circuit, Where Does the Power Formula Come From? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/9omx07AKH5Q
- Joe Robinson Training. EAL Electrical Science & Principles Level 2 Revision. (2019, October 4). What is Electricity? Part Three: Which way do electrons flow? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/2ZlfXE_PZOQ
- Joe Robinson Training. EAL Electrical Science & Principles Level 2 Revision. (2019, February 27). What is Electricity? Part Two: The Atomic Structure of Copper. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/XBJQ_JfJ57Y
- Joe Robinson Training. EAL Electrical Science & Principles Level 2 Revision. (2018, October 30). What is Electricity? Part One: The Structure of an Atom. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/XBJQ_JfJ57Y
- KQED. (2020, May 5). Slide Energy. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/1GDsb_kJR20
- Manocha Academy. (2019, July 22). Magnetism. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/bBKYZFtcWHc
- Manocha Academy. (2020, March 2). Magnetic Effect of Electric Current. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/v7hWt9F3WcY
- Maribel, M. (2020, August 11). The Math You’ll Use in Chemistry. (First 5 minutes only.) [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/B2EnaKgF08M
- National STEM Centre. (2015, January 17). Static Electricity Demonstration - The Electric Sausage. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/CHGaMutanKE
- Science Bits. (2015, March 20). Video Lab: Magnetic forces. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/Mp0Bu75MSj8
- Science Shorts. (2017, January 27). Magnetic Fields, Flux Density & Motor Effect - GCSE & A-level Physics. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/o0yfYTtR6go
- Seeker. (n.d.) Inside The World's Largest Particle Accelerator. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/328pw5Taeg0
- Shenoy, M. (n.d.) Electric power & energy. Khan Academy. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/p1XG7LopGkg
- Spark Fun Electronics. (2016, November 2). Adventures in Science. Electric Power. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/p8JQTLkV5C8
- Spark Fun Electronics. (2016, October 12). Adventures in Science. What is Voltage? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/z8qfhFXjsrw
- Spark Fun Electronics. (2016, October 19). Adventures in Science. What is Electric Current? [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/kYwNj9uauJ4
- Spark Fun Electronics. (2016, October 26). Adventures in Science. Ohm’s Law. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/8jB6hDUqN0Y
- Summers, A. (2014, March 1). Transposition of Formulae Part 1. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.tradeskills4u.co.uk
- Summers, A. (2014, March 17). Transposition of Formulae Part 2. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.tradeskills4u.co.uk
- Taylor, C. (n.d.) Electricity Basics. Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Ohm's Law. https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/voltage-current-resistance-and-ohms-law/all
- Technology Student.com. (2002-2022). Test Instruments. https://technologystudent.com/elec1/metre1.htm
- The Physics Classroom. (n.d.) Electricity: Electric Circuits. https://www.physicsclassroom.com/calcpad/circuits/problems
- TutorVista. (2010, April 27). Conductors Insulators and Semi-Conductors. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/8Pnsbh0DrE4
- W CLN. (2013, April 9). Ohm's Law Experiment. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/48_CqnhRbww
- Woodward, C. (2021, October 21). Explain that stuff. Electricity. https://www.explainthatstuff.com/electricity.html