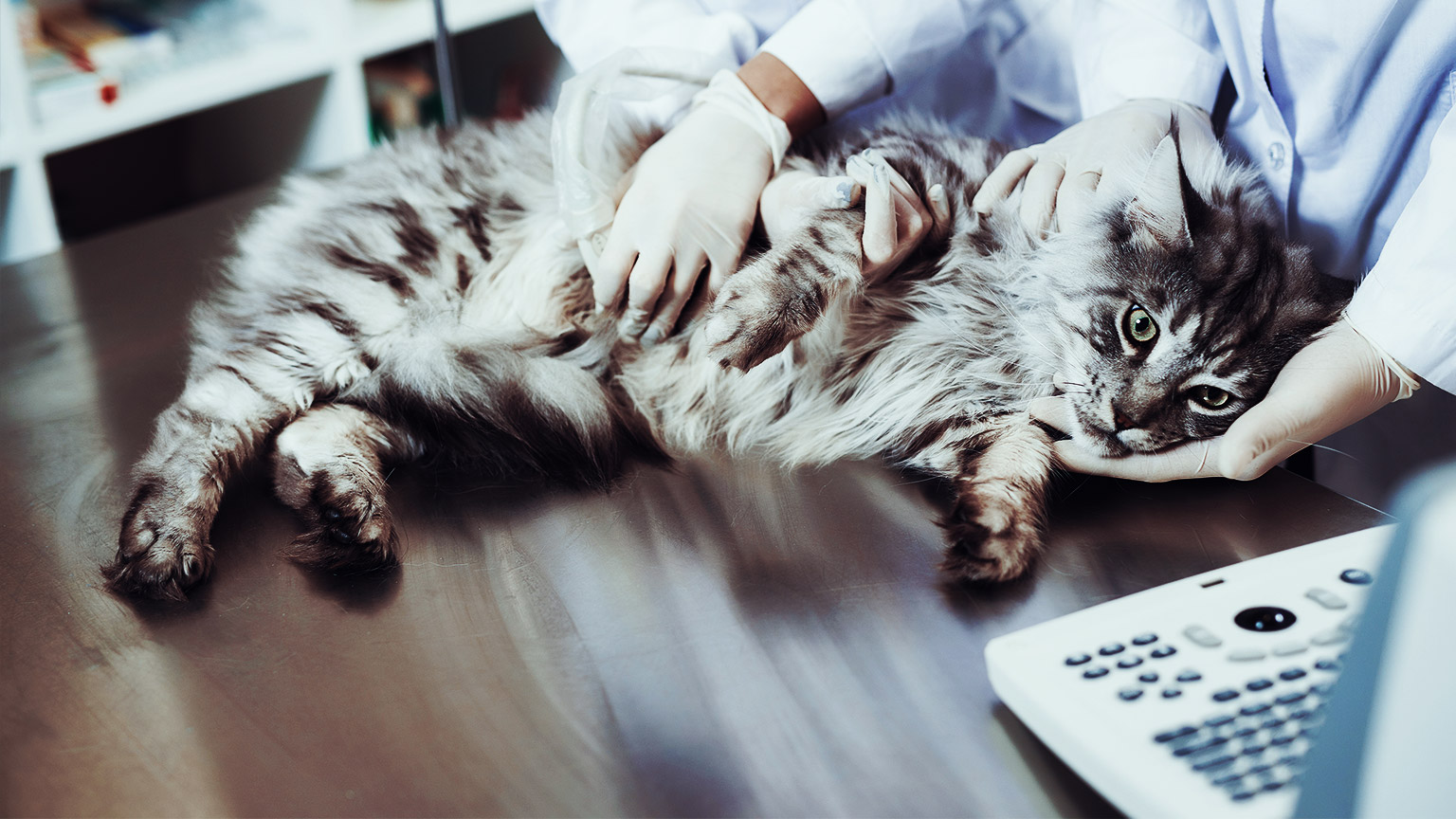
Part of your role in maintaining the health and safety of people entering your clinic is to ensure all animals are healthy. This means you will need to be constantly monitoring for signs of ill health or abnormal conditions. Observation is the first step in this process, once you have developed the observational skills, this will help you determine the behaviour of the animal as well as see any physical changes to the animal’s appearance.
When an animal comes in for examination, you will need to ensure you know and understand what characteristics to look for when it comes to infectious diseases. Infectious diseases require a host, which is a person, animal, fish, bird, or arthropod, which is, or can, become infected with, and give sustenance to, a disease-causing organism.
There are two aspects of infectious diseases. They include:
Pathogens
Disease causing microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses, found commonly in sewage, hospital waste, run-off water from farms, and in water used for swimming. Most pathogens are parasites (live off the host) and the diseases they cause are an indirect result of their obtaining food from, or shelter in, the host. Larger parasites (such as worms) and not called pathogens.
Opportunistic organisms
Opportunistic microorganisms are typically non-pathogenic microorganisms that act as a pathogen in certain circumstances. They lay dormant for long periods of time until the host's immune system is suppressed and then they take that opportunity to attack.
What to look for
When conducting an examination, you need to be considerate of external features and vital signs. The following table illustrates the characteristics of each.
| External features | Vital signs |
|---|---|
| Body condition score | Temperature |
| Coat or skin condition | Pulse |
| Ear, eye, nose presence or absence of discharge | Respiration |
| Eye condition and response to light | Capillary refill |
| Presence of wounds, lesions, swelling | Hydration status |
| Heat | |
| Smell of breath |
Physical examination
Many of the animals you may examine are familiar and regular clients and contrary, they may never have been to the clinic before. It is important you never assume the animal will not bite you, no matter how well you know them, always examine with caution. If you have any doubt during the examination process, you should always ask the veterinarian or experienced member of the team to assist you.
When you are preparing for examination, ensure you have consulted with the owner and discuss what they have noticed to also be considerate of when you are ready to conduct a physical examination. Once you have gathered enough information and observed the behaviour of the animal, you are ready to conduct the physical exam.

This will include checking on the following:
- temperature
- pulse rate
- respiratory rate
- abnormal lung sounds
- ears
- eyes
- mouth (if the animal will let you).
The following table illustrate the temperature, pulse, and respiratory rates of the following animals. When a physical examination is being conducted, you will need to ensure you are aware of what the normal rates are for each of these animals, so you are able to rule out an issue involving them.
| Animal | Temperature | Pulse Rate | Respiratory Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dog | 38.3 – 38.7 D Celsius | 60 – 180 bpm | 10 – 30 bpm |
| Cat | 38.0 – 38.5 D Celsius | 110 – 180 bpm | 20 – 30 bpm |
| Rabbit | 38.5 – 40.0 D Celsius | 180 – 300 bpm | 30 – 60 bpm |
| Horse | 37.2 – 38.3 D Celsius | 28 – 44 bpm | 10 – 24 bpm |
Once you have completed the first half of the examination, you will then proceed to check rest of the body including:
- skin
- limbs
- neck
- head
- chest
- stomach
- tail
- back
- paws.
Triaging the patient
When an animal comes into the clinic, it is very important that you are able to recognise the signs of potential infectious disease that the animal may be presenting. This is also known as triage; assessing the severity of the illness to determine how best to treat them. Some patients may present minor conditions, while others may be presenting signs of a more serious condition. Use the indicators we have discussed as a guide to support the triage process. The triage process is very important because if there is an emergency, the animal will need to be treated immediately. There are special forms each clinic will have for triage purposes.
When the animal is suffering a serious condition, in addition to the signs we have discussed, the animal may also present signs of:

- chewing or licking own body excessively
- defensive behaviours
- drooling and regurgitating food
- excessive drinking
- excessive rolling
- general changes in normal behaviour or routines
- lameness
- listlessness or disinterest in surroundings
- presence of blood, swelling, excessive heat
- reluctance or refusal to eat or drink
- reluctance to move
- sweating
- yelping or other vocalising when touched or if animal attempts to move or perform particular tasks or grooming.
It is important you understand the various types of common infectious diseases that companion animals may be diagnosed with. Many of these diseases can be passed from animal to animal, however, some can be passed to humans from animals, this is known as zoonoses. As an animal care worker, it is important you understand what types of infectious diseases are transmissible to both animals and people. We are now going to look at:
- The type of disease and correct scientific identification,
- The animal which it effects.
- A description of each.
- Means of transmission.
- Symptoms.
- Whether or not it is classified as zoonosis.
- Treatment.
- Prevention.

Scientific name
Bordetella Bronchiseptica
Susceptible animal:
Dogs (canines)
Description
Canine infectious respiratory disease complex, commonly known as kennel cough is a transmissible infection amongst the canine species
Means of transmission:
The disease is transmitted through. Direct contact inhalation of cough or indirect contact such as sneeze droplets, licking objects contaminated with bacteria/viruses.
Symptoms:
The common signs or symptoms of this disease include:
- a strong cough, often with a “honking” sound (this is the most obvious symptom)
- runny nose, sneezing
- lethargy
- loss of appetite
- low fever.
Zoonoses:
While this disease is contagious between canines, it cannot be transmitted to humans.
Treatment:
In many cases, Bordetella can clear on its own, but it can also be treated with antibiotics and cough suppressant medication to ease the symptoms.
Prevention:
There is a vaccine available to treat Bordetella, in addition to oral, intranasal vaccines. It is best to ensure vaccination for Bordetella are carried out annually, especially if the dogs are attending boarding kennels and grooming salons.

Scientific name:
HCanine parvovirus
Susceptible animal:
Canines (dogs/ puppies)
Description
The Canine Parvovirus (CPV) is a disease that causes severe gastrointestinal illnesses commonly detected in puppies aged between 6-20 weeks. The virus attacks the small intestine causing the destruction of the gut lining. In addition, the virus can also attack the bone marrow causing the inability to produce white blood cells to fight infection. It is important to note, that this virus can be transmitted to older dogs, although it is most commonly seen in puppies.
Means of transmission
The CPV is highly contagious and is transmitted through faeces of infected animals. Dogs can pick up the virus from their own paws, sniffing the ground on walks or in dog parks in addition to it being picked up on people’s shoes. It is very important to understand, this virus is extremely durable and can survive on surfaces for a long period of time.
Symptoms
The common signs and symptoms of CPV include:
- severe, often bloody, diarrhea
- loss of appetite
- abdominal pain and bloating
- fever or low body temperature (hypothermia)
- vomiting
Zoonoses:
While this disease is contagious between canines, it cannot be transmitted to humans.
Treatment
The treatment of CPV will often require the animal to be kept in an animal hospital where they can receive round the clock are with fluids and antibiotics and in some cases blood transfusions to replenish the diminishing white blood cells from the bone marrow. The severity of the virus will determine the level of care that is required.
Prevention
In the case of the CPV, prevention is better than cure. The best form of defense for this virus is early vaccination of puppies. Puppies should receive a combination of shots which will include a vaccination for CPV every 3-4 weeks from when the puppy is 6 weeks old until it reaches 16 weeks. The puppy will then require a booster vaccine.

Scientific name:
Feline calicivirus
Susceptible animal:
Cats (felines)
Description:
Feline upper respiratory disease complex is commonly known as cat flu. It is highly contagious that causes a mild to severe infection in the respiratory system in cats. It is common in shelters and targets younger cats. In most cases, the cat is likely to recover completely, however, some mutations of this virus can be fatal.
Means of transmission:
Felines that have been diagnosed with this disease, can transmit it to other felines through cough and sneeze droplets and through sharing bedding and food/water bowls.
Symptoms:
Signs and symptoms felines may exhibit if that have contracted this disease include:
- sneezing
- conjunctivitis
- rhinitis
- lacrimation
- salivation
- oral ulcers.
Zoonoses:
While this disease is contagious between felines, it cannot be transmitted to humans.
Treatment:
There is no treatment to stop the virus, and in many cases the cat can be treated at home, however if the virus is severe, the cat will require intensive care in an animal hospital.
Prevention:
Vaccines may not prevent a cat from contracting a virus completely, however it will lessen the severity should it be contracted. The vaccine is usually given in addition to others that are used to treat viruses which can be given via injection or nasally.

Scientific name:
Panleukopenia
Susceptible animal:
Felines (Cats)
Description:
HFeline panleukopenia is an extremely infectious disease that commonly effects cats, mainly kittens. This virus infects, attacks, and kills cells in the animal’s body that are known for multiplying and dividing such as white blood cells found in bone marrow, cells in the intestines and a developing fetus.
Means of transmission:
Felines that have been diagnosed with this disease, can transmit it to other felines through a range of routes including through faecal-oral, direct contact with faeces from litter trays, and shared water, and food bowls. In addition, the disease is can be transmitted via contaminated surfaces from urine or vomit along with humans that have virus contaminants on their clothing or shoes. The virus is exceptionally durable and can last up to a year on surfaces if they are not cleaned properly. Any area that has been contaminated with this virus must be cleaned with bleach as this is the only substance that can completely remove it. If a cat has been diagnosed with this virus, they will need to be isolated immediately and any area that it has been in contact with has been thoroughly cleaned to avoid the transmission to other cats.
Symptoms:
Felines that have contracted this disease will display symptoms that include:
- loss of appetite
- extreme lethargy
- vomiting
- fever
- diarrhoea (sometimes bloody).
Zoonoses:
While this disease is contagious between felines, it cannot be transmitted to humans.
Treatment:
While it can be treated, it is very difficult especially for kittens that have not been vaccinated under 8 weeks, the likelihood of survival is very slim. Older cats that may have contracted the virus will need to undergo special intensive care treatment to combat the virus.
Prevention:
When it comes to this virus, prevention is better than cure Vaccination against the virus while the felines are still kittens is the best defense against this virus. It is advised kittens undertake their vaccinations between 6-8 weeks and follow up vaccines at 16 weeks to help build their resilience to this virus.
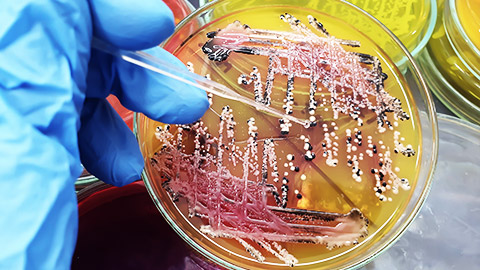
Scientific name:
Salmonellosis
Susceptible animals:
- reptiles
- amphibians
- poultry
- horses
- pigs
- cattle
- rodents
- birds
- dogs
- cats.
Description:
Salmonellosis is a type of bacterial group that effects the intestinal/ digestive tract of the body of many animals. It is a bacterial disease caused by Salmonella. Salmonella is naturally in the intestines of many different animals. There are several strains of Salmonellosis that can cause illness to animals should they come infected.
Means of transmission:
The most common means of transmission for Salmonellosis is through ingestion of contaminated food and water or contact of infected faeces that can shed onto the animal’s fur, skin, or scales. The bacteria can also survive on surfaces and can be picked up from any surface the infected animal has come into contact if surfaces are not cleaned properly after the bacteria has been diagnosed or identified.
Symptoms:
- diarrhea that may contain blood or mucus.
- lethargy
- vomiting
- fever.
Zoonoses:
Salmonellosis is categorised as zoonoses because animals that have been infected can pass it to humans. Commonly, people can pick up the bacteria from touching infected surfaces, bedding, pet food including treats, and faeces without washing their hands thoroughly. Some animal products humans eat may also carry the bacteria and can infect people making them very ill. Some people may have reptiles and amphibians as pets and can also become infected without touching the animal because the water in the tank or the aquarium has been exposed. Salmonellosis does not discriminate with who is susceptible to contracting it. That means, virtually anyone is at risk of contracting the bacteria when proper care is not taken. However, people who have a lower immunity from an ongoing illness are at risk of serious infection in addition to those who are elderly and children.
Treatment:
If a companion animal has been diagnosed with Salmonellosis, it will need immediate veterinary attention, with plenty of fluids and antibiotics- depending on the severity of the illness. In extreme cases, animals may need to be kept in an animal hospital or veterinary clinic over night where they can be monitored closely.
Prevention:
One of the best means of preventing salmonella is through minimising exposure and thorough cleaning of bedding, food and water bowls and areas which house animals. In addition to cleaning practices, you will also need to ensure you are maintaining appropriate hygiene with correct handwashing and cleaning of surfaces after treating animals. Finally, you should ensure you have isolated the animal and any other animals that may have come into contact with infected animals until they have been cleared of infection. Aviod feeding your dog raw or undercooked meat, as this is a risk factort.
Scientific name:
Toxoplasmosis gondii
Susceptible animals:
- Felines (cats)
Description:
Toxoplasmosis is caused by a protozoan parasite called Toxoplasma gondii. Wild and domestic cats are the most susceptible hosts for this parasite. Cats become infected initially after they have ingested prey that has also been infected with it. Once the parasite enters the body of the cat, it begins to attack the digestive tract and multiplies on the wall of small intestine. As it multiplies, it produces oocysts which are then released into the cat’s faeces. However, once it has been shed, it is not immediately infectious it must go through a sporulation which can take up to five days and it is after this stage, it becomes infectious. The following diagram illustrates the lifecycle of toxoplasmosis.
Means of transmission:
The most common form of transmission for toxoplasmosis through contact or ingestion. The most common exposure it to cat faeces containing oocysts, coming into contact with the faeces and than subsequent ingestion. Cats can become infected by eating infected rodents, birds or other small animals.
Symptoms:
- fever
- loss of appetite
- lethargy
- pneumonia
- yellowish tinge to the skin
- inflammation in the eye.
Zoonoses: Toxoplasmosis can be transmitted from animals to humans therefore it is categorised as a zoonoses.
Humans can become infected with toxoplasmosis if they ingest food that has been contaminated and not washed properly and touching faeces from litter that have been through the sporulation process. Pregnant women should avoid changing cat litter trays as they are at risk of contracting it.
Treatment:
Treatment for toxoplasmosis is usually a course of antibiotics
Prevention:
Cat litter needs to be changed regularly, preferably twice a day to ensure sporulation does not take place and avoid allowing cats to hunt and roam to avoid the risk of them ingesting an animal that may be infected with toxoplasmosis. Always practice effective hygiene, use gloves, and warm water soap and disinfectant.

We are now going to look at parasites. Parasites are very common in companion animals and can be an issue all year round, but some can be more prevalent during the warmer months. When discussing parasites, there are internal and external ones that commonly effect companion animals.
Internal versus external
Each type of parasite that effects our companion animals causes a range of health concerns and if left untreated can be quite dangerous for them. It is essential companion animals have received the appropriate treatment for each type of parasite to ensure they remain in a healthy condition.
Internal parasites are those that live inside the body of the animal and can attack a range of internal organs of the animal and may include:
- hookworm
- roundworm
- tapeworm
- whipworm
Scientific name:
Ancylostoma caninum (dogs) or Ancylostoma tubaeforme (cats).
Susceptible animals:
- dogs
- cats
- rodents
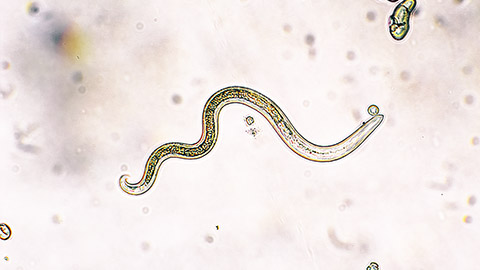
Hookworm is an internal parasite that attack the digestive system. There are two types of hookworm that effect cats and dogs in Australia and they are called Ancylostoma and Uncinaria. Adult worms are roughly 16mm in length and very thin. They attach themselves to the intestines of dogs and cats and feed off blood and the intestinal wall. Hookworms if left untreated can cause serious illness or even death. Animals may pick up the parasite when they have been exposed to other animals that have not been appropriately treated for hookworm and defecate on the ground, for example at a park.
Means of transmission: Ingestion of contaminated food is one of the most common means of transmission. Usually, once the food has been ingested, the egg also known as an ova enters the body and the larvae penetrate through the skin or the digestive system. It can be picked up off the ground and transmitted to unborn puppies and kittens via the placenta if the mother has ingested the ova. If the mother has contracted hookworm after she has given birth, it can be passed to the litter while she is lactating and infect the young.
The following image illustrates the transmission of hookworm.
Symptoms:
- diarrhoea often (with blood and mucous)
- anaemia
- lethargy
Zoonoses: Hookworm is highly contagious and can be transmitted from animals to humans making hookworm a type of zoonoses.
Humans contract hookworm when they touch contaminated soil from infected faeces with their bare hands or feet. Humans may also contract hookworm if they ingest contaminated soil from poorly washed food.
Treatment:
An effective wormer can help treat hookworm which will then need to be kept up regularly because the larvae and newly contracted worms will not be affected by the treatment therefore an additional dose is required. In extreme circumstances, animals with severe side effects such as anaemia will require hospitalization and may require a blood transfusion.
Prevention:
Like many other diseases or parasites, prevention is better than cure and it is highly recommended the animals are given a good quality wormer to target hookworm and prevent it from becoming an issue. Puppies and kittens will need to partake in regular worming regimes evert 2 weeks until they reach 12 weeks of age. They will then need to receive a worming treatment once a month until they reach 6 months and finally, the will require a treatment once every three months when they reach full maturity.
Take a short break from the reading and watch the following video based on hookworms in dogs.
Scientific name:
Toxocara canis (dogs) or Toxocara cati (cats)
Susceptible animals:
- Canines
- Felines.
Description:
Roundworms are white and cylinder in shape and closely resemble spaghetti. Roundworms are some of the most common types of parasites that affect dogs and cats. The adult roundworms live and feed off the small intestines. Roundworms have been known to pass through to the lungs causing the animal to cough. Roundworms can produce up to 85,000 eggs a day!
Means of transmission:
Roundworms are transmitted through eating food that has been affected with the parasite. Pregnant and lactating mothers can pass the parasite to their offspring making puppies and kittens very susceptible to infestation. Roundworm in feline’s can be transmitted through contact with faecal matter picked up from litter trays. Birds and rodents may also harbor the parasite and can infect a cat or dog if they hunt and eat birds or rodents.
Symptoms:
- diarrhea
- vomiting
- weight loss
- swollen abdomen
- dull fur.
- Poor condition with potbelly
- Stunted growth
- Intestinal obstruction
- Lack of appetite
Zoonoses: Roundworm is highly transmissible to humans, especially pregnant women, children, and those who are immunocompromised, making it a type of zoonoses.
Humans can contract roundworms from touching or handling soil that has been contaminated with faeces from an infected animal. Roundworms in humans can have serious health implications including issue with their eyes, lungs, heart and neurological concerns.
Treatment:
If the animal has been diagnosed with roundworm, they will need to be treated with specific deworming drugs to combat the parasite. Treatment will need to be carried out with a strict deworming regime to ensure all roundworms and eggs have been treated.
Prevention:
Preventing roundworm is achievable with a consistent worming regime, especially with pregnant and lactating mothers and their offspring. Worming should commence for puppies and kittens at 2 weeks og age. Worming should continue fortnightly until 12 weeks on age. After 12 weeks of age worming is continued monthly until 6 months of age. At 6 months of age worming is continued 3 monthly for the remainder of the pets life. Some products are combined with heartworm and therefore worming may need to be given monthly.
Fun Fact!
Did you know, roundworm eggs can remain dormant in cat litter trays, sandpits, and soil for years! Some of these eggs can attach themselves and hide in animal tissue and remain dormant enabling them to activate even after treatment.

Scientific name:
Trichuris vulpis
Susceptible animals:
- Canines
- Felines (Although very rare)
Description:
Whipworms are like many of the other internal parasites that attach themselves to an animal’s small intestine. Whipworms get their name from their unique shape; they are long, thin and enlarged at one end.
Means of transmission:
Animals can become infected with whipworm if they have eaten a contaminated animal, ingested contaminated water or come into contact and ingested infected faeces. Puppies and kittens are most at risk from contracting whipworm as the parasite can be passed on from the mother during pregnancy and when lactating.
Symptoms:
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhea often with blood
- Lethargy
- Abdominal bloating
Zoonoses:
While whipworms are highly contagious between animals, they cannot be transmitted to humans.
Treatment:
Should an animal be infected with whipworm; they will require a treatment regime starting from two treatments that have been spanned over 3-4 weeks. If animals are severely ill from exposure to whipworms, they may require stay in an animal hospital to offer treatment.
Prevention:
Prevention is the most essential measure to take when combat whipworm. Regular worming is essential to keep whipworm from infecting the animal, especially for pregnant and lactating mothers.
Fun fact!
Did you know, whipworms can float? When you suspect the animal has a whipworm, a floatation test can be carried out on a stool sample to see if the parasite rises to the surface.

Scientific name:
Dipylidium caninum
Susceptible animals:
- Canines
- Felines
Description:
Tapeworms are long flat worms that attach themselves to the animal’s intestines. Tapeworms are unique compared to other internal parasites because their body is made up of different parts, with each part of the body having its own reproductive organs. When an animal has been infected with a tapeworm, you may often see a small white worm attached the anus of the animal (similar in appearance to a grain of rice). The worms may also appear in the animal’s faeces or in bedding. Tapeworms come in various species and when they infect the animal, do so at different stages.
Means of transmission:
Initially, tapeworms attach themselves to a host, whether it is another animal or fleas. When the animal has eaten an infected source, the parasite is ingested and starts to feed of the intestines of the new host. Dipylidium caninum is the tapeworm that attaches itself to fleas as the initial host. When the fleas attach themselves to the skin of animals, the parasite then passes from the flea into the animal when the animal is grooming itself and ingests the flea.
Symptoms:
- Licking or biting their anus
- Irregular itching of their behind, perhaps by dragging or ‘scooting’ along the floor
- Weight loss even though they are eating normally
- Vomiting: this can be caused if segments make their way into the stomach
- White or cream ‘grain size’ segments on the fur, particularly by their tail, or in their bed
- White or cream ‘grain size’ segments, or worms, in their stool
Zoonoses:
Tapeworm can be transmitted to people therefore categorizing it as zoonoses. While it can be transmitted, it is very unlikely unless the person has swallowed an infected flea. Children are most susceptible to contracting tapeworm, however, if the animal is regularly treated for fleas, chances of transmission are minimised.
Treatment:
The treatment for tapeworm is relatively straightforward and can be treated with a special drug called praziquantel which can be given orally or as an injection.
Prevention:
As with all intestinal worms, prevention is better than cure. Animals should partake in a regular worming and flea treatment regime to keep these parasites from infesting the body.
Fun fact!
Did you know, tapeworms can grow up to 71cm in length!
External parasites
You will now have developed an understanding of internal parasites. We are now going to look at the parasites that are visible with the naked eye that exist on the skin or fur of companion animals.

Scientific name:
- Paralysis tick: Ixodes holocyclus
- Brown tick: Rhipicephalus sanguineus
- Bush tick
Susceptible animals:
Description: Ticks are small parasites that that attach to the skin and suck blood from the host. In Australia there are three main types of ticks that pose a threat to domestic animals, they include:
- Paralysis tick
- Brown tick
- Bush tick.
The paralysis tick most dangerous of the ticks and is found along the east coast of Australia, including the south-east coastal areas in Victoria. Once the paralysis tick attaches to a host, it starts to inject a toxin. If the tick is left long enough, it will start to cause paralysis of the animal which can, if left untreated, lead to death. Tick saliva is neuro and cardiotoxic what means it has a deleterious effect on the heart and nervous system causing ascending paralyses.
There are also bush ticks and brown dog ticks that may be present in Victoria, but they are not as harmful as the paralysis tick. These ticks will suck blood and become engorged, but do not cause paralysis. They may cause a local irritation and sore at the site of attachment, but if there are high enough numbers, they can also cause anaemia due the amount of blood loss. The following image sliders illustrate the stages in which a tick goes through as they are feeding off the host.
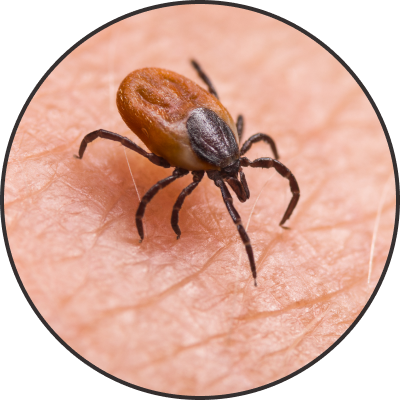

Unengorged
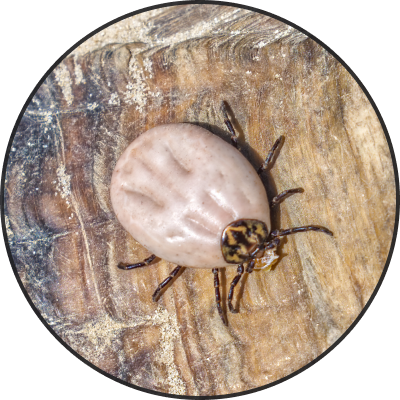

Partially engorged
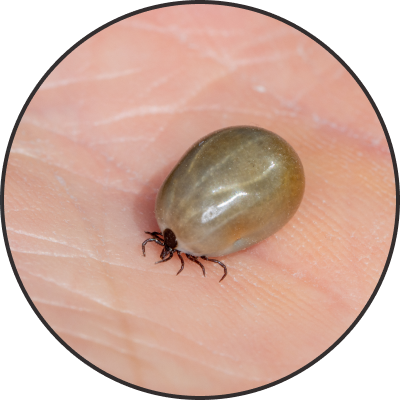

Fully engorged
Means of transmission:
Ticks usually attach themselves to a host, whether an animal or a person and begin to feed off their blood. The tick firmly attaches itself often burying its head into the surface of the hosts skin inserting the feeding tube and secretes saliva. The salvia of a tick has anesthetic properties which allows the tick to feed going virtually unnoticed. Whatever disease the host animal has, the tick will ingest and when it drops off to find a new host, will transfer that disease to the next one.
Symptoms of paralysis tick toxicity:
- A change in the sound of the bark or voice
- Gagging/retching
- Regurgitation or vomiting (sometimes with froth)
- Breathing changes – difficulty breathing often with a characteristic grunting sound
- Wobbliness in the back legs which worsens to paralysis and an inability to stand (sometimes owners describe it as ‘my dog has gone in the back legs’)
- Excessive salivation/drooling (sometimes frothing around the mouth area)
- Coughing (sometimes it is a moist cough)
- Not eating
- Progressive paralysis to include the forelegs
- Other abnormal behaviour
- Agitation
- Sound of meow may change
- Unusual breathing pattern with a soft grunt at the end of expiration (breathing out)
- Weakness, though this is typically less obvious to owners early on
- Gagging or retching
- Salivation
- Not eating
- More advanced stages include a more obvious difficulty in walking, staggering and swaying
- Other abnormal behaviour
Treatment:
If an animal has been bought in suspected to have been exposed to a tick, they will need immediate medical attention where they receive a tick antiserum in addition to and intravenous fluid therapy (IV drip) and a period of hospitalization where they can be appropriately monitored and treated.
Prevention:
Prevention is far better than cure in the case of ticks. Wherever possible known tick habitats should be avoided, grass kept short, and animals avoided walking in bush areas. In addition to avoiding these habitats, tick prevention treatment should given to animals. It is important to note however, the same medication given to a dog should not be given to a cat and vice versa. These medications have been specifically designed to suit the type of animal they are prescribed for and may pose risk to them if they are prescribed or administered incorrectly.
Fun fact!
Did you know, female ticks are responsible for causing paralysis?
Scientific name

Ctenocephalides felis
Susceptible animals:
- Dogs
- Cats
- Guinea
- rabbits
- birds
Description:
Fleas live, breed, multiple on the skin of animals. Fleas can transfer tapeworms, cause bacterial infections, and can result in the animal to lose its fur and make it very irritated. Fleas can multiply very quickly and reach maturity within a few short weeks, when the animals become infested, this can be hard to control, especially in the home.
Fleas are a blood sucking parasite. Fleas can jump and move rapidly throughout the fur of the animal.
Means of transmission
Fleas will spend most of their time on the host animal with an endless blood supply. Other animals are likely to catch fleas from an infested environment such as their bedding or carpet as opposed to direct contact with another animal.
Symptoms:
- Skin damage
- Itchiness
- Skin irritation
- Infection
- Anaemia (blood loss)
Treatment:
Fleas and lice are relatively easy to treat with on-the-spot treatments available. All veterinary practices will be equipped with the appropriate treatments for animals that come in with fleas or lice in the form of oral or topical medication.
Prevention:
Using preventative flea treatment will
Scientific name:
Microsporum canis/ Dermatophytosis
Susceptible animals:
- Canines (dogs)
- Felines (cats)
- Birds
- Rodents
- Rabbits
Description:
Ringworm is a type of skin and scalp disease that is caused by a type of fungi. Ringworm is identified by the unique ring liked shape that appears on the skin in the form of rash. The fungus that is responsible for spreading ringworm is found in spores in the environment.
Means of transmission:
Ringworm is transmitted through direct contact with another animal that has been infected. The animal may also contract ringworm through objects that have also been in contact with the fungus such as bedding, food bowls, blankets and so on. Ringworm even spreads through the shedding of infected hair.
Symptoms:
- Hairless patches on the skin
- Circular and irregularly shaped areas of scabs and hair loss
- Dry brittle hair
- Rough and brittle claws
Zoonoses:
Ringworm is highly contagious and can be transmitted from animals to humans therefore it is classified as a zoonoses. Humans with animals that have been diagnosed with ringworm are likely to contract it through the direct contact they have with their pets.
Treatment:
Animals that have been infected with ringworm will require topical and oral medication as well as thorough cleaning of the effected area. Oral medication is the best form of treatment for ringworm and the animal will need to complete their course of oral medication to ensure the infection does not recur.
Prevention:
Preventing ringworm can be tricky, however, preventing the spread of infection can be carried out through regularly cleaning of the animal’s bedding or housing, along with brushing hair and keeping brushes clean. You will also need to ensure once an animal has been brushed, the area has been cleaned incase the fur is contaminated, and another animal or person picks it up in transmission.
Fun fact!
Did you know, ringworm is not actually a worm at all? It is fungus that breeds in warm damp environments such as soil.
The following image are examples of how ringworm would look on animals and people if they are infected,
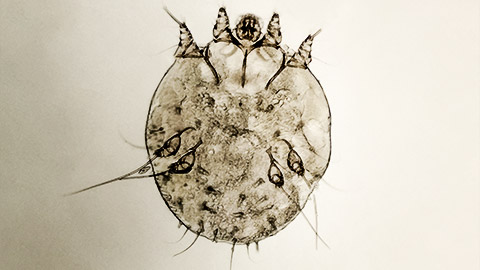
Scientific name:
Sarcoptes scabiei.
Susceptible animals
- dogs
- cats
- horses
- goats
- pigs
- birds.
Description
Scabies or what it is also known as Sarcoptic mange, is a parasite that can be carried by most mammals including foxes, wombats, dogs, and cats. The parasite/ mite lives on the host animal burrowing under the skin of the animal causing severe itching and hair loss on the host.
Means of transmission
Scabies is highly contagious and causes immense itching on the animal The scratching leads to skin infections which make the problem worse and requires treatment. The mite is passed between animals by direct contact with an infected animal, however in some cases, especially when the months are cooler, the might can survive in the environment, then it will attach to the animal if it contacts the same area
Symptoms:
- Intense scratching
- Rash
- Crust formation
- Hair loss.
Zoonoses:
Scabies is classified as zoonotic disease because humans can contract it from their pets, the mites can transfer from the animal to the human causing the same itchy rash.
Treatment:
Topical treatment including medicated sprays and washes can be used to treat scabies/ mange in addition to chewable tablets.
Prevention:
Animals should have their skin regularly checked and avoid skin to skin contact with other animals that may have been exposed to the mites. In many cases, animals may pick up the parasite through hunting other animals or reading/by-passing animals in holding facilities or kennels, especially if the animal has been severely neglected.
The following images provide a visual of how scabies can effect animals
